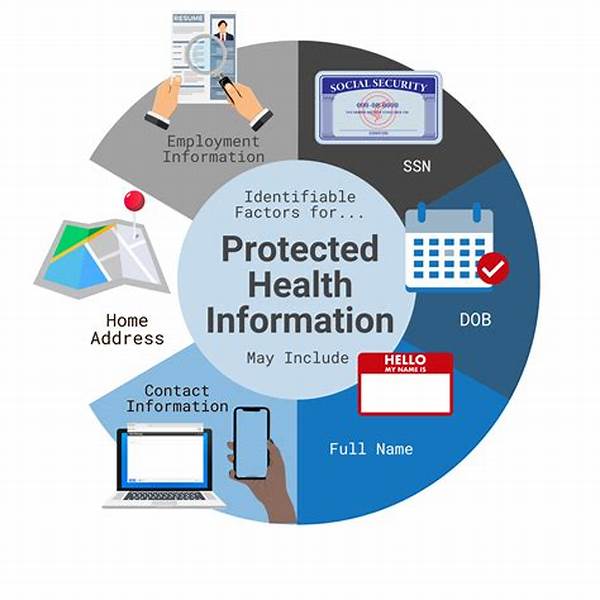
The safeguarding of sensitive health information is a responsibility that is paramount in today’s digital age. The pervasive integration of technology into healthcare has transformed how medical data is stored, accessed, and shared. With this evolution comes the duty to ensure that patient information remains confidential and secure. This article endeavors to highlight the multifaceted approach required to protect this crucial data, delving into the standards, challenges, and practices pivotal to safeguarding sensitive health information. Such proactive measures are essential to maintain public trust and comply with regulatory imperatives.
Read Now : Variable Dosing Protocols In Healthcare
The Importance of Safeguarding Health Data
Securing sensitive health information is critical not only for compliance with regulations but also for maintaining trust in the healthcare system. Patients entrust their personal health details to professionals and institutions, expecting confidentiality. Any breach can lead to identity theft, financial loss, or a damaged reputation. Protecting sensitive health information requires adherence to stringent protocols and the implementation of advanced security technologies. This includes encryption, access controls, and regular audits to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Furthermore, employee training and awareness programs are essential in reinforcing the significance of data protection practices across all levels of an organization.
With the increased interoperability of health systems, data is shared across platforms, facilitating better patient outcomes but also exposing information to potential vulnerabilities. Thus, healthcare organizations must balance the benefits of connectivity with the necessity of protecting sensitive health information. The holistic approach encompasses both technological safeguards and policy development, ensuring that data protection becomes an integral part of the organizational culture. Ultimately, the goal is to ensure that sensitive health information is handled with the highest standard of ethical and professional responsibility.
Key Strategies for Data Protection
1. Encryption Techniques: Employing strong encryption protocols ensures that even if data is intercepted, deciphering it remains a formidable challenge, thereby protecting sensitive health information effectively.
2. Access Control: Implementing role-based access limits the number of individuals who can view or modify sensitive health data, thereby protecting sensitive health information by reducing the risk of internal breaches.
3. Regular Audits: Routine audits and assessments help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with data protection regulations, fortifying efforts in protecting sensitive health information.
4. Employee Training: Providing continuous education to healthcare staff about security practices and the importance of protecting sensitive health information minimizes human error and enhances data security.
5. Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to national and international standards, such as HIPAA, aligns operational practices with legal requirements for protecting sensitive health information efficiently.
The Role of Technology in Protecting Health Information
In the digital age, technology plays a pivotal role in protecting sensitive health information. Innovative solutions such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and machine learning are now being explored to strengthen data security. Blockchain technology, for instance, offers a decentralized framework that records transactions securely and transparently, reducing the risk of data tampering. Machine learning algorithms can predict potential security threats by analyzing patterns, offering preemptive solutions before breaches happen.
Read Now : Genomic Data Integration In Healthcare
Moreover, as the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand within healthcare, ensuring devices are secure against cyber threats becomes imperative for protecting sensitive health information. This places an onus on manufacturers to build robust security features and on healthcare providers to configure device settings correctly. However, despite the allure of cutting-edge technologies, human oversight remains crucial. Technology must complement rather than replace the vigilance required in protecting sensitive health information, ensuring that healthcare systems remain resilient against evolving cyber threats.
Addressing Challenges in Data Protection
Protecting sensitive health information isn’t easy, given the fast pace of tech advancement and the slyness of cybercriminals. It’s like watching over a treasure chest, where the jewels are patients’ vital health details. Balancing rapid data sharing with airtight security feels like juggling. Encryption and firewalls aren’t just geek speak—they’re basically your secret service agents against data prying. And regular training? It’s like reminding everyone on the ship to lock up before leaving the helm. It’s not about paranoia; it’s about making sure no sneaky pirate lands a score. Even with all this, trust remains the glue that holds the healthcare-patient relationship tight, making protecting sensitive health information the Holy Grail we’re all searching for.
Ensuring Compliance in Health Information Protection
Regulatory Frameworks and Standards
The landscape of protecting sensitive health information is heavily influenced by regulatory frameworks such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These regulations set forth guidelines that healthcare organizations must follow to ensure patient information is adequately protected. Compliance not only prevents legal ramifications but also demonstrates the entity’s commitment to data security and patient confidentiality. Detailed standards dictate how data should be managed, accessed, and shared, requiring healthcare providers to build comprehensive data protection strategies. Adhering to these regulations signifies a proactive approach in safeguarding sensitive health data, instilling confidence in patients and stakeholders alike.
Organizational Practices for Data Security
Healthcare organizations must integrate stringent data protection measures within their operational frameworks to effectively secure sensitive health information. This involves cultivating a security-conscious culture where employees at all levels are trained and aware of their role in maintaining data integrity. Implementing technologies such as intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication, and secure communication channels further fortifies an organization’s defenses. Regular security assessments and audits form a pivotal part of this approach, identifying weaknesses and enhancing existing protocols. These practices, when combined with adherence to regulatory requirements, solidify an organization’s resolve in protecting sensitive health information, thereby preserving its reputation and ensuring patient trust.
Conclusion on Protecting Sensitive Health Information
In conclusion, protecting sensitive health information is a multifaceted endeavor that demands attention to regulatory frameworks, technological advancements, and organizational practices. A robust data protection strategy underscores the importance of vigilance and adaptability in an ever-evolving digital landscape. Achieving this necessitates both a commitment to continual improvement in security measures and fostering a culture of awareness and responsibility among healthcare professionals. Ultimately, safeguarding sensitive health information is an ongoing commitment that reinforces trust in the healthcare system and ensures compliance with legal mandates.
Healthcare providers must remain vigilant, consistently reviewing and updating their data protection protocols in response to emerging threats. Fostering a collaborative environment where all stakeholders, from IT professionals to healthcare workers, understand their role in protecting sensitive health information is crucial. This collective effort ensures that healthcare delivery remains efficient while maintaining the highest standards of privacy and security, reinforcing public confidence in the healthcare system’s ability to protect the most personal of data.