The landscape of modern medicine is continuously evolving with the integration of traditional and complementary treatments. The intersection of pharmaceuticals and herbal remedies presents a realm where scientific rigour is required to unravel the myriad complexities involved. Understanding the biological basis of drug-herb interactions is paramount to ensure patient safety and maximize therapeutic efficacy across various treatments.
Read Now : “differences In Drug Formulations”
Exploring the Interactions
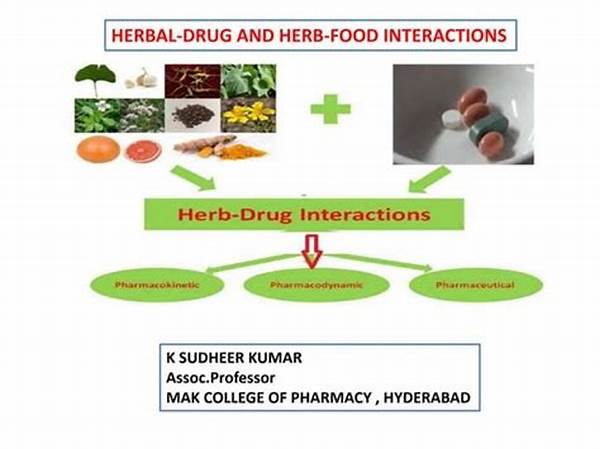
The biological basis of drug-herb interaction primarily revolves around the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic processes within the human body. Pharmacokinetics pertains to how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes substances. Herbs that induce or inhibit drug-metabolizing enzymes can significantly alter these processes, leading to variations in drug efficacy and toxicity. For instance, St. John’s Wort is well-documented to induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, potentially reducing the effectiveness of certain medications like oral contraceptives.
Pharmacodynamics, on the other hand, involves how drugs or herbal components affect the body. Herbal compounds may exhibit synergistic or antagonistic effects when combined with pharmaceutical agents. This interaction can lead to unexpected physiological responses, either enhancing the desired therapeutic effects or precipitating adverse reactions. For example, the anticoagulant effects of warfarin can be potentiated by garlic supplements, increasing the risk of bleeding.
The investigation into the biological basis of drug-herb interaction is a complex and continuously evolving field. Considering the vast number of possible herb-drug combinations, research requires a meticulous and methodical approach. Clinical trials designed to ascertain the safety and efficacy of such combinations are critical in developing guidelines for their concurrent use in therapeutic regimens.
Key Mechanisms Involved
1. Enzyme Induction and Inhibition: The biological basis of drug-herb interaction is significantly influenced by herbs altering enzyme activity. This can lead to increased metabolic rates of drugs, thereby diminishing their efficacy, or slowed metabolism which may increase drug toxicity.
2. Transporter Proteins: Drug-herb interactions can affect transporter proteins integral to drug absorption and distribution. The biological basis of drug-herb interaction ensures that these variations can impact the plasma concentration of drugs.
3. Receptor Binding Modulation: Certain herbs possess active compounds that may compete with drugs for receptor binding. This highlights a critical facet of the biological basis of drug-herb interaction, potentially altering drug response.
4. Synergistic Effects: Herbal components may enhance the pharmacological effects of drugs, which is a core aspect of the biological basis of drug-herb interaction. This can be beneficial or harmful depending on the context.
5. Antagonistic Effects: Conversely, some herbs could reduce drug effectiveness. Understanding the biological basis of drug-herb interaction aids in anticipating such outcomes and mitigating potential therapeutic conflicts.
Challenges and Considerations
Unveiling the biological basis of drug-herb interaction requires addressing significant scientific and practical challenges. Diverse chemical constituents in herbs and their variable concentrations present considerable hurdles in standardizing research outcomes. Coupled with individual genetic variations, these interactions become even more complex, necessitating personalized approaches to medicine.
Healthcare practitioners should exercise vigilance when prescribing conventional drugs alongside herbal supplements. It is of utmost importance to maintain open communication with patients regarding all substances they are consuming. Education on the potential for adverse interactions forms a pivotal part of clinical responsibilities. Consequently, the need for comprehensive databases consolidating the current knowledge on drug-herb interactions is critical for informed clinical decisions.
Read Now : Customized Integrative Health Solutions
Advancements in analytical technologies and methodologies, such as high-throughput screening and bioinformatics, are likely to augment our understanding of the biological basis of drug-herb interaction. Through targeted research efforts, the overarching goal remains to enhance patient outcomes by integrating safe, effective, and evidence-based traditional practices with modern medical treatments.
Impacts on Pharmacological Paradigms
The integration of herbal remedies into conventional medical frameworks presents a dual-edged sword, underscoring both potential benefits and risks. The biological basis of drug-herb interaction offers a scientific lens to evaluate these dual phenomena critically. Understanding these interactions not only ensures patient safety but also prioritizes innovative pharmacological paradigms that could encapsulate the best of both worlds.
Such insights promote the rational use of both drug types, harmonizing complementary practices with established medical treatments. This equilibrium can lead to breakthroughs in treatment modalities, offering new therapeutic avenues while preserving the integrity and efficacy of pharmaceutical interventions. The intricate dance between drugs and herbs becomes an opportunity for modern medicine to evolve towards greater inclusivity and holistic healing approaches, rooted in scientific exploration and validation.
Challenges in Research and Application
The exploration into the biological basis of drug-herb interaction is fraught with complexity, considering the wide array of pharmacologically active compounds present in herbs. These complexities challenge researchers to design rigorous studies that can reliably assess the interactions at play. Standardization in herbal concentrations, variability in human metabolism, and the differential expression of genetic enzymes add layers of intricacies that demand sophisticated analytical approaches.
Clinical implementation of knowledge on the biological basis of drug-herb interaction necessitates informed consent and patient education. Physicians must navigate these interactions carefully to avoid adverse effects that could diminish therapeutic outcomes. Moreover, the necessity for interprofessional collaboration is paramount, ensuring that researchers, pharmacists, and clinicians work synergistically to merge traditional and modern medical wisdom safely and effectively.
Conclusion on Integration
In conclusion, the biological basis of drug-herb interaction unveils a frontier rich with both challenge and promise. By delineating the intricate biochemical and physiological pathways involved, the scientific community can better anticipate and mitigate adverse effects, maximizing patient benefits. As we edge towards a more integrative medical practice, fostering familiarity and respect towards both herbal and pharmaceutical therapies will be vital.
Overall, a nuanced understanding of the biological basis of drug-herb interaction can provide valuable insights into developing safer and more effective treatment protocols. By continuing to delve into this intersection with scientific investigation and clinical prudence, there lies potential to enhance healthcare outcomes while honoring diverse medicinal traditions.