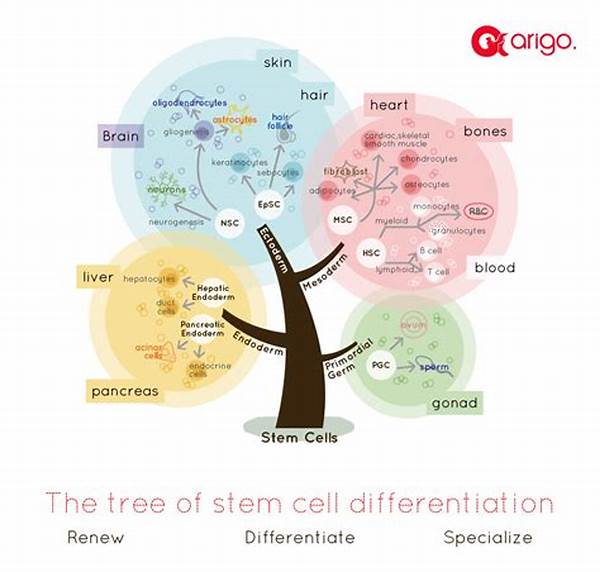
The advancement of medical science has paved the way for groundbreaking discoveries, one of which is stem cell research in regenerative medicine. This field holds the promise of revolutionizing the treatment of myriad diseases and debilitating conditions. As scientists delve deeper into the capabilities of stem cells, the potential to regenerate damaged tissues and organs brings new hope to patients and healthcare providers worldwide. With the rising incidence of chronic diseases and the quest for effective treatment modalities, the significance of stem cell research in regenerative medicine cannot be overstated.
Read Now : Tailored Health Interventions Via Genomics
The Potential of Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell research in regenerative medicine involves the use of cells with the innate ability to differentiate into various cell types, offering the unique potential to repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. By investigating the capabilities and applications of different types of stem cells, researchers aim to harness their regenerative powers. There is a keen focus on studying embryonic stem cells, adult stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Each type of stem cell presents specific advantages and challenges that researchers must navigate. The exploration of these cells’ potential has led to promising advances in treating conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. However, amidst the potential, ethical considerations remain a central issue, requiring an ongoing dialogue to ensure that scientific progress aligns with societal values.
Key Benefits and Challenges of Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
1. Therapeutic Potential: Stem cell research in regenerative medicine offers the unparalleled potential to regenerate tissues, potentially curing diseases once deemed incurable.
2. Personalized Medicine: Advances in this field could lead to personalized treatment plans tailored to individual genetic make-up, enhancing the efficacy of therapeutic interventions.
3. Ethical Dilemmas: The application of embryonic stem cells raises ethical concerns, necessitating rigorous ethical frameworks and guidelines to govern research practices.
4. Technological Limitations: Despite significant progress, technological constraints still pose challenges, requiring sustained research and innovation to overcome these barriers.
5. Long-term Impacts: The long-term effects of stem cell therapies remain under investigation, necessitating extensive clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy before widespread implementation.
Emerging Trends in Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
The field of stem cell research in regenerative medicine is continuously evolving, with emerging trends shaping its future trajectory. One key area of advancement is the refinement of techniques to generate induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This innovation has minimized ethical concerns associated with embryonic stem cells, as iPSCs are derived from adult cells. Furthermore, researchers are focused on optimizing the differentiation process to ensure greater precision and consistency in developing specific cell types for therapeutic use. Explorations into the microenvironment’s role in supporting stem cell function have also gained traction, highlighting the significance of the extracellular matrix in regulating cell behavior. As technological advancements continue, collaborations between interdisciplinary teams will likely drive further innovations, enhancing the efficiency and applicability of stem cell research in regenerative medicine.
Casual Perspectives on Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
Stem cell research in regenerative medicine is seriously changing the game in the medical world. It’s like scientists have unlocked the potential to fix and even grow new parts of the body, which is wild. The fact that these cells can turn into any other cell type means the possibilities are endless, from healing spinal injuries to curing blindness.
1. Mind-blowing Potential: The idea of turning stem cells into any type of cell is like having a biological magic wand!
2. Ethical Drama: Not everyone is thrilled about using embryonic cells; talks are still heated around these ethical grey areas.
3. Tech Breakthroughs: New tech keeps popping up to help scientists better control how these cells grow and change.
4. Team Effort: Collaboration is key, with experts from many fields joining forces to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Read Now : Herbal Anxiety Treatment Options Explored
5. Future Vibes: The long-term possibilities of stem cell therapies are seriously exciting, with potential cures for major diseases on the horizon.
6. Game Changer: If stem cell therapies can fix things like heart disease or Alzheimer’s, it could totally transform healthcare.
7. Trials and Errors: They’re still testing and learning, meaning it’s not all smooth sailing yet—trial and error is part of the process.
8. Patient-Centric: This research could lead to treatments tailored specifically to individuals, like a custom health solution.
9. Funding Frenzy: There’s a rush of investment flowing into research labs to accelerate these medical breakthroughs.
10. Hope for Many: For patients and families battling chronic conditions, the potential of stem cells offers a beacon of hope for effective treatments.
Ethical Considerations in Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
The exploration of ethical considerations within the domain of stem cell research in regenerative medicine presents a complex discourse that intertwines scientific inquiry with moral philosophy. The utilization of embryonic stem cells, in particular, has ignited debates surrounding the moral status of embryos. This dialogue is vital as it prompts stakeholders to evaluate the balance between scientific advancement and ethical responsibility. The crux of the debate revolves around ensuring that research adheres to principles of respect for life, integrity, and equity. With numerous countries implementing regulatory frameworks, the contention lies in harmonizing these diverse legal and ethical landscapes to facilitate global research collaboration. In addition, informed consent from donors is paramount, emphasizing the need for transparency and autonomy in decision-making processes.
Current Applications and Innovations in Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
Current applications in stem cell research in regenerative medicine have demonstrated promising results, signaling a transformative phase in therapeutic interventions. Breakthroughs in cellular reprogramming have enabled the generation of patient-specific cells, reducing rejection risks and enhancing treatment efficacy. Moreover, innovations such as organoid technology have permitted the study of disease mechanisms in a controlled environment, expediting drug discovery and development. These advancements hold potential for not only treating degenerative diseases but also addressing trauma-induced injuries through tissue engineering. As the field progresses, interdisciplinary collaboration is essential to scale these innovations from bench to bedside, ensuring that stem cell research translates into viable clinical solutions for patients worldwide.
Summary of Stem Cell Research in Regenerative Medicine
The landscape of stem cell research in regenerative medicine is both intricate and promising, marked by substantial scientific and clinical strides. This research domain is characterized by its potential to transcend traditional treatment modalities, offering hope for regenerative therapies across a spectrum of diseases. By harnessing the inherent plasticity of stem cells, researchers are unlocking new frontiers in tissue engineering, paving the way for personalized and precision medicine that addresses individual patient needs. Nevertheless, this journey is fraught with challenges, including ethical considerations, technological constraints, and the necessity for stringent regulatory compliance. As the field expands, the collective endeavor to surmount these hurdles is vital to realizing its full therapeutic potential, ultimately transforming the landscape of modern medicine.