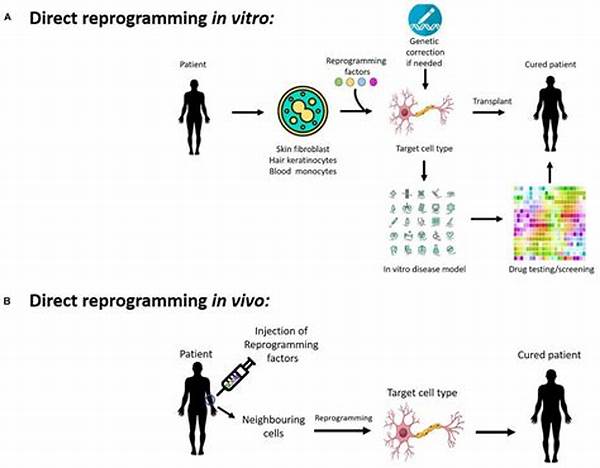
Cellular reprogramming in vitro denotes a groundbreaking advancement in modern biotechnology. It refers to the process by which mature, specialized cells are transformed into a different cell type, often returning them to a pluripotent state similar to embryonic stem cells. This powerful technique holds immense potential for regenerative medicine, offering new avenues for understanding disease mechanisms and developing innovative therapeutic strategies.
Read Now : Calming Botanical Remedies For Sleep
The Mechanism of Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
The concept of cellular reprogramming in vitro is anchored in the ability to manipulate cell fate through the introduction of specific transcription factors. These factors are pivotal in inducing a series of epigenetic changes that alter the gene expression profile of the target cells. In essence, this process unlocks the inherent plasticity of cells, enabling them to acquire new identities. The laboratory setting provides a controlled environment wherein researchers can meticulously orchestrate and monitor these cellular transformations. Through in vitro reprogramming, fibroblasts, a type of cell found in connective tissue, can be coaxed into becoming induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). This discovery has far-reaching implications, not only in understanding developmental biology but also in the potential restoration of damaged tissues. Researchers continue to refine the methodologies involved in cellular reprogramming in vitro, aiming to enhance efficiency and reproducibility, thus paving the way for future clinical applications.
Advancements and Applications of Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
1. Cellular reprogramming in vitro is revolutionizing drug discovery processes by providing patient-specific cell models to test pharmacological effects, leading to more accurate and personalized treatments.
2. With cellular reprogramming in vitro, scientists can derive various cell types from iPSCs, including neurons, cardiomyocytes, and pancreatic cells, offering promising prospects for cell replacement therapies.
3. The technology of cellular reprogramming in vitro enables the study of genetic diseases through the creation of disease-specific cells, thus facilitating a deeper understanding of pathogenesis and potential interventions.
4. In cancer research, cellular reprogramming in vitro assists in the identification of novel targets by studying tumor formation and progression, offering insights into personalized cancer treatments.
5. Cellular reprogramming in vitro also holds potential in toxicological studies, allowing for the examination of chemical effects on human cells in a controlled environment, thus enhancing safety evaluations.
Ethical and Technical Considerations in Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
The application of cellular reprogramming in vitro raises ethical considerations, primarily concerning the potential for human cloning and genetic modification. As cells are reverted to a stem-cell-like state, the possibility of creating entire organisms from these cells poses significant moral questions. Regulations and guidelines must be rigorously developed and adhered to in order to circumvent potential misuse. Technically, the process of cellular reprogramming in vitro is not without its limitations. The reprogramming efficiency remains a critical barrier, with only a small fraction of cells achieving the desired transformation. Additionally, ensuring the stability and safety of reprogrammed cells is paramount, as they may pose risks such as tumorigenesis. As research progresses, these challenges must be addressed to harness the full potential of cellular reprogramming in vitro.
Slang Perspectives on Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
1. Dude, cellular reprogramming in vitro is like a magic trick—turning regular cells into super-flexible ones!
2. Imagine cells jamming in a lab, flipping identities like it’s a game of switcheroo, thanks to cellular reprogramming in vitro.
3. Cellular reprogramming in vitro is kinda like giving cells a reboot—taking them back to basics, so they can level up!
4. Bro, this cellular reprogramming in vitro thing is the real deal—it’s like transforming a caterpillar into a butterfly in a petri dish.
Read Now : Effective Prescription Reminder Techniques
5. If cells were DJs, cellular reprogramming in vitro would be them spinning old tracks into fresh beats.
6. No kidding, man, cellular reprogramming in vitro is shaking up the science world like soda on a hot day.
7. With cellular reprogramming in vitro, it’s like blowing up the balloon of possibilities in medicine!
8. Think of cellular reprogramming in vitro as hitting the ‘undo’ button on a cell’s life decisions.
9. Pumping up cellular reprogramming in vitro is like turning a simple sketch into a masterpiece.
10. Cellular reprogramming in vitro is where science gets funky, bending reality into something mind-blowingly cool!
Challenges in the Field of Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
As the field of cellular reprogramming in vitro expands, numerous challenges persist. The complexity of human cells is mirrored in the intricacies of the reprogramming process. One prominent issue is the low efficiency of converting differentiated cells into induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), a pivotal aspect of reprogramming. Current techniques often require a prolonged duration and result in a small percentage of successful transformations. Addressing these efficiency concerns is critical for the widespread application of this technology. Moreover, ensuring the genetic and functional stability of reprogrammed cells is crucial, particularly when considering therapeutic uses. Researchers must diligently refine protocols to mitigate the risk of unintended genetic alterations that could lead to oncogenesis or other adverse effects. Furthermore, the in vitro environment, although controlled, does not fully replicate the complex interactions occurring in vivo, which may affect the behavior of reprogrammed cells. Continued research and development are necessary to overcome these technical and biological hurdles.
Breakthroughs in Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro Research
Recent years have witnessed remarkable breakthroughs in cellular reprogramming in vitro research. Novel approaches have emerged, including the development of small molecules that enhance reprogramming efficiency without the genetic manipulation of cells. This advancement holds promise in minimizing potential risks associated with current reprogramming techniques. Additionally, researchers are exploring combinatorial strategies that utilize transcription factors in conjunction with microenvironmental cues to optimize reprogramming outcomes. Another significant leap is the integration of single-cell analysis to dissect the heterogeneity of reprogramming trajectories, thereby providing deeper insights into the underlying mechanisms. The convergence of cellular reprogramming in vitro with cutting-edge technologies such as CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing further propels the field forward, offering tailored solutions for disease modeling and regenerative medicine. These innovations underscore the dynamic nature of cellular reprogramming research, propelling it steadily towards translational applications.
Summary of Cellular Reprogramming In Vitro
Cellular reprogramming in vitro marks a paradigm shift in biomedical research, offering unprecedented opportunities for studying cellular plasticity and disease modeling. By employing transcription factors to revert differentiated cells to a pluripotent state, this technology opens new frontiers in regenerative medicine and personalized therapies. Since the advent of this technique, scientists have made significant progress in refining methods to bolster its efficiency and safety. Ethical considerations remain paramount, necessitating comprehensive guidelines to govern its application. Despite challenges, the potential for cellular reprogramming in vitro to revolutionize healthcare is immense. Advances in the field continue to unfold, driven by a commitment to understanding the fundamental principles of cell identity and reprogramming mechanisms. The integration of novel techniques such as small molecule modulators and advanced genomic tools exemplifies the dynamic progression of the discipline. As researchers push the boundaries of what is possible, the prospects for cellular reprogramming in vitro are boundless, underscoring its vital role in the future of medicine.