The application of scientific evidence in medicine serves as the cornerstone for contemporary medical practice. As healthcare continues to evolve in complexity, the reliance on evidence-based practices ensures that treatments and interventions are safe, effective, and optimized for patient outcomes. A rigorous approach to medical research and clinical trials contributes substantially to validating the efficacy of new treatments, ensuring they are grounded in scientific reality rather than conjecture or anecdote.
Read Now : Made-to-order Herbal Remedy Schemes
Importance of Scientific Evidence in Medical Practice
The importance of scientific evidence in medicine cannot be overstated. It is the foundation on which reliable medical practices are built, distinguishing validated medical approaches from those lacking empirical support. This evidence emerges from meticulous research, including randomized controlled trials, observational studies, and systematic reviews, each contributing to the robustness of clinical guidelines. Without such evidence, medical practice risks reliance on outdated techniques or the adoption of novel approaches without adequate validation, potentially compromising patient safety.
Furthermore, scientific evidence in medicine empowers healthcare providers to make informed decisions tailored to each patient’s unique circumstances. By integrating individual patient data and broader research findings, medical professionals can customize treatments that align with the best available evidence. This integration not only enhances treatment efficacy but also fosters patient trust in medical professionals, as decisions are transparently grounded in proven research.
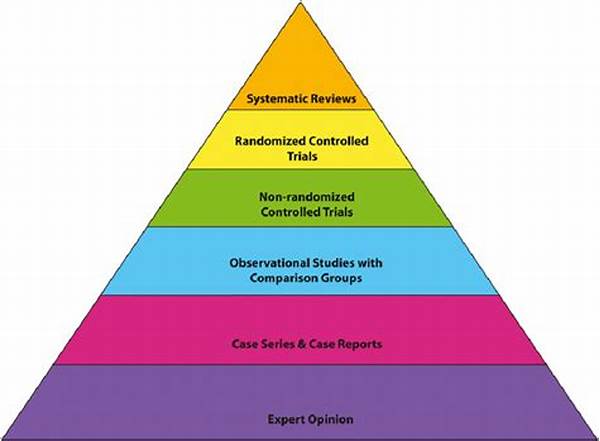
Key Concepts in Scientific Evidence in Medicine
1. Clinical Trials: These are essential for testing new treatments. Through scientific evidence in medicine, clinical trials assess safety and effectiveness.
2. Systematic Reviews: Comprehensive reviews that compile extensive research to produce reliable medical conclusions. They enhance the quality of scientific evidence in medicine.
3. Meta-Analysis: Statistical techniques that combine results from various studies, providing more precise estimates of treatment effects and augmenting scientific evidence in medicine.
4. Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs): These provide high-quality evidence by minimizing bias in evaluating treatment efficacy, thus forming a critical part of scientific evidence in medicine.
5. Observational Studies: Studies that help identify correlational patterns in health outcomes and contribute to the growing body of scientific evidence in medicine.
Advances and Challenges in Scientific Evidence in Medicine
Scientific evidence in medicine has seen significant advancements, particularly with the advent of precision medicine. This approach tailors treatment protocols to individual genetic, environmental, and lifestyle differences, further elevating patient care. Such advancements underscore the dynamic evolution of medical science, continuously challenging established norms and prompting ongoing research and validation.
However, challenges persist. The complexity of diseases, potential biases in research, and the ethical considerations in trial designs often complicate the development of definitive scientific evidence in medicine. To address these issues, collaboration among global research institutions and adherence to strict ethical guidelines is necessary. Such measures ensure that the pursuit of new evidence remains both scientifically sound and ethically responsible.
Perspectives on Scientific Evidence in Medicine (Slang Style)
1. Scientific evidence in medicine is like the Google map for doctors—keeps them on the right track.
2. Without solid evidence, medicine would be like shooting in the dark.
3. Think of evidence in medicine as the cheat codes for better health outcomes.
4. Evidence-based medicine is the real MVP in healthcare—no cap.
Read Now : Reducing Complexity In Medication Schedules
5. Scientific evidence makes sure we ain’t playing guessing games with people’s lives.
6. It’s like having receipts for every medical decision made—trustworthy stuff.
7. Dodgy evidence in medicine? That’s a big, fat nope.
8. Evidence is the boss of medicine, setting the rules straight.
9. Sketchy treatments without evidence? That’s a hard pass, fam.
10. With top-notch evidence, medicine hits different—trust the process.
The Role of Scientific Evidence in Modern Therapies
In the modern medical landscape, the role of scientific evidence in medicine is pivotal, particularly in the development of therapies and treatments. The foundation of evidence-based medicine dictates that decisions in healthcare are derived from well-conducted research and empirical data. Such an approach ensures that therapeutic interventions are not only efficacious but also hold the trust of both practitioners and patients, substantiating the reliability of medicine as a science.
The methodologies involved in accumulating scientific evidence in medicine include rigorous clinical trials, comparative studies, and peer-reviewed research, each playing a crucial part in establishing effective treatment modalities. As the medical community continues to grapple with emerging diseases and complex health issues, the reliance on solid scientific evidence becomes ever more paramount. The integrity of healthcare systems depends on this evidence to navigate the intricacies of treatment efficacy, patient safety, and healthcare policy.
Evaluating the Validity of Scientific Evidence in Medicine
Evaluating the validity of scientific evidence in medicine involves scrutinizing the research methodologies employed to accumulate this evidence. Trustworthy evidence emanates from well-designed studies characterized by robust methodologies, including randomization, replication, and peer review. These elements ensure that findings are not only valid and reliable but also applicable to diverse patient populations. Hence, healthcare professionals must be adept at critically appraising the quality of evidence, recognizing the differences between high and low evidence quality. They must also understand how to incorporate this evidence into patient care, balancing clinical expertise with empirical data to optimize treatment outcomes.
Summary
In summary, scientific evidence in medicine is the backbone of informed and effective healthcare practices. Through diligent research and methodological rigor, this evidence provides a solid foundation for medical professionals to deliver care that is safe, effective, and customized to individual patient needs. It is through this continual process of evidence gathering and validation that advancements in medical science are achieved, benefiting both patients and the broader healthcare system. The obligation to maintain stringent standards in evidence creation and evaluation remains crucial, ensuring that the practice of medicine evolves in response to new discoveries and societal health challenges.
The reliance on scientific evidence in medicine not only augments the credibility of healthcare practices but also plays a critical role in shaping public health policies. It strategically informs guidelines that govern patient care, resource allocation, and research priorities, serving the dual purpose of safeguarding individual and community health. The interplay between evidence-based practice and policy formation underscores the holistic role of scientific evidence in medicine, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research, education, and interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing public health objectives.