Clinical trials for health products constitute a critical component of the medical research ecosystem, serving as a cornerstone in the evaluation of new health-related interventions. These trials provide the scientific evidence necessary to assess the safety and efficacy of various products ranging from pharmaceuticals to medical devices. The process ensures that only those products that are both effective and safe reach the public. The importance of this rigorous process cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts patient safety and the advancement of medical science.
Read Now : **in Vitro Reprogramming Protocols Development**
The Importance of Clinical Trials for Health Products
Clinical trials for health products are essential in bridging the gap between scientific research and practical application. Through a structured methodology, these trials assess products in a controlled environment, enabling researchers to make informed decisions about their viability. Clinical trials for health products involve several phases, each designed to address specific research questions. Initial phases focus on safety, while later stages ascertain efficacy and optimal usage. The culmination of these trials provides a comprehensive understanding of the product’s potential impacts on health and informs regulatory approval processes.
Moreover, clinical trials for health products contribute to the ever-evolving landscape of medical treatments. By rigorously evaluating new products, trials not only validate their therapeutic benefits but also identify possible side effects. This dual role is indispensable in refining existing treatments and paving the way for innovative therapies. They also play a crucial role in reinforcing public trust in medical products, as their transparent and systematic nature assures consumers that products have undergone extensive testing and scrutiny.
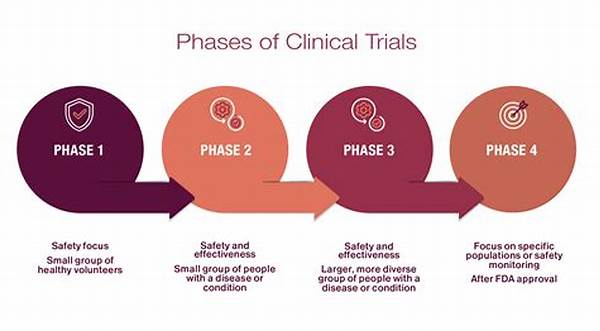
The Phases of Clinical Trials for Health Products
1. Phase 1: Conducted with a small group of volunteers to evaluate the product’s safety, dosage, and side effects. At this juncture, clinical trials for health products primarily focus on safety.
2. Phase 2: Involves a larger group of participants to assess efficacy and further evaluate safety. This phase of clinical trials for health products establishes a preliminary understanding of the product’s therapeutic effects.
3. Phase 3: Conducted with large groups to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, and compare the product to commonly used treatments. Successful completion of this phase is critical for clinical trials for health products seeking regulatory approval.
4. Phase 4: Takes place post-approval to monitor the product’s effectiveness in the general population and gather information on long-term use and side effects. This phase ensures the continued safety of clinical trials for health products.
5. Phase 5: Encompasses comparative effectiveness research and implementation studies to optimize the use of the product. This is a relatively recent addition to the spectrum of clinical trials for health products.
Regulatory Oversight in Clinical Trials for Health Products
Regulatory oversight plays an indispensable role in ensuring the integrity of clinical trials for health products. Governmental agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or the European Medicines Agency (EMA) are tasked with enforcing stringent standards and guidelines throughout the trial process. These agencies meticulously review trial protocols, monitor progress, and assess outcomes to ensure adherence to ethical and scientific principles. This oversight extends to the design, execution, and reporting phases of clinical trials for health products.
In addition, ethical considerations feature prominently in regulatory oversight. The protection of human subjects is paramount, with frameworks such as informed consent and Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) established to safeguard participants’ rights and well-being. Furthermore, transparency in reporting findings is mandated, promoting public confidence and facilitating the broader dissemination of knowledge. Consequently, regulatory authorities ensure that clinical trials for health products not only meet scientific criteria but also align with societal expectations of ethics and trustworthiness.
Challenges Facing Clinical Trials for Health Products
Clinical trials for health products encounter a myriad of challenges that can influence their execution and outcomes. Recruitment of diverse participant populations is one notable challenge. Ensuring representation of various demographic groups is vital to accurately assess a product’s efficacy across different segments of the population. Additionally, the complexity and length of clinical trials often lead to significant financial and logistical demands. This necessitates careful planning and efficient resource management to sustain trials through to completion.
Read Now : Interpersonal Skills For Adherence Enhancement
Furthermore, the advent of personalized medicine has introduced new variables into the trial process. Tailoring products to individual genetic profiles demands innovative trial designs and analytics approaches, complicating traditional methodologies. Despite these challenges, continuous advancements in technology and research methodologies offer promising avenues for overcoming these obstacles. Bridging these gaps is vital to the advancement of clinical trials for health products, ultimately enhancing their impact on global health.
The Role of Technology in Clinical Trials for Health Products
The integration of technology in clinical trials for health products is transforming the landscape of medical research. Innovations such as electronic health records, wearable devices, and telemedicine have enhanced data collection and monitoring capabilities. These technologies facilitate real-time analysis and remote patient tracking, optimizing the efficiency of clinical trials for health products. Consequently, trials are becoming more adaptive and responsive to emerging data trends.
In addition, technology has amplified patient engagement by providing accessible platforms for education and communication. Participants can easily access trial information, report symptoms, and engage with research teams, enhancing compliance and retention rates. This interaction fosters a collaborative environment, ensuring that clinical trials for health products are inclusive and patient-centered. As technology continues to evolve, its integration into clinical trials augments the capabilities of researchers, promising a future of more precise and effective health solutions.
Ethical Considerations in Clinical Trials for Health Products
Ethical considerations form the backbone of clinical trials for health products, ensuring the protection of human subjects and the integrity of research. The informed consent process underlines ethical conduct by ensuring that participants are adequately informed about the trial’s purpose, procedures, risks, and benefits. This transparency empowers potential subjects to make voluntary, well-informed decisions about their participation.
Moreover, Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) play a crucial role in safeguarding ethical standards during clinical trials for health products. IRBs meticulously review trial protocols to ensure that the rights and welfare of human subjects are preserved. They also monitor ongoing trials for compliance with ethical guidelines, with the authority to pause or terminate studies that deviate from approved standards. This oversight ensures that clinical trials for health products uphold the principles of respect for persons, beneficence, and justice, vital to the research’s credibility and trustworthiness.
Summary of Clinical Trials for Health Products
In conclusion, clinical trials for health products are foundational to the advancement of medical science, bridging the gap between scientific innovation and public health. These trials adhere to a structured methodology that ensures a thorough evaluation of safety and efficacy. Through various phases, clinical trials for health products provide a comprehensive understanding of a product’s potential impact, informing regulatory decisions and guiding clinical practices.
Moreover, the rigorous scientific and ethical frameworks guiding clinical trials for health products reinforce public confidence in medical advancements. Despite challenges such as recruitment and trial complexity, ongoing technological innovations and methodological advancements provide promising solutions to these obstacles. As clinical trials for health products continue to evolve, they promise to enhance global health outcomes by ensuring that only safe and effective products reach the market. These trials remain an essential and dynamic component of medical research, steering the future of healthcare towards improved patient outcomes and innovative therapeutic solutions.