Advancements in Personalized Medicine Through Genomics
Personalized medicine through genomics represents a paradigm shift in how we approach disease diagnosis and treatment. By leveraging insights from an individual’s genetic makeup, healthcare professionals can tailor therapies that are more effective and have fewer side effects compared to traditional treatments. The fundamental principle of personalized medicine through genomics is rooted in the understanding that each person’s genetic profile is unique, impacting their susceptibility to certain diseases and their response to specific treatments.
Read Now : **regulation Of Gene Expression**
In recent years, technological advancements have significantly enhanced our ability to analyze genetic data, enabling the development of highly personalized therapeutic strategies. This innovation holds immense potential for improving patient outcomes across various medical fields, including oncology, cardiology, and neurology. For instance, in oncology, personalized medicine through genomics allows for the identification of specific genetic mutations in tumors, facilitating the selection of targeted therapies that can improve survival rates and quality of life for cancer patients.
Furthermore, personalized medicine through genomics also plays a critical role in preventive healthcare. By identifying genetic predispositions to certain conditions, individuals can make informed lifestyle choices and healthcare decisions that may reduce their risk of developing such conditions. This proactive approach not only enhances individual well-being but also contributes to the overall efficiency of healthcare systems by reducing the burden of chronic diseases. The continued integration of genomic data into clinical practice promises to further advance the field of personalized medicine, offering new avenues for research and patient care.
Key Components of Personalized Medicine Through Genomics
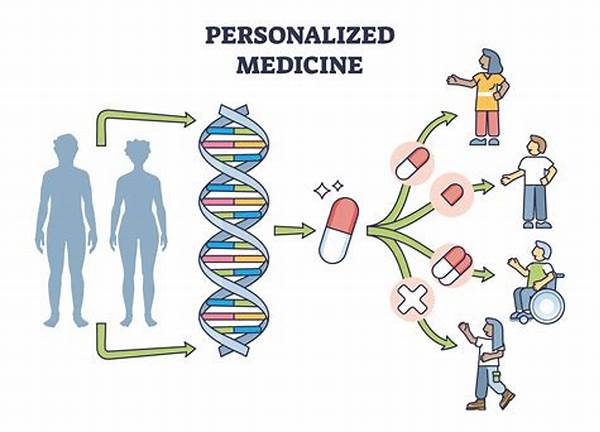
1. Individualized Treatment Plans: Personalized medicine through genomics involves creating treatment plans tailored to an individual’s genetic profile, thus enhancing the efficacy and reducing the adverse effects of therapies.
2. Genomic Data Utilization: The use of genomic data in personalized medicine assists in identifying genetic mutations that may influence disease progression and treatment response.
3. Targeted Drug Development: Personalized medicine through genomics aids pharmaceutical companies in developing drugs tailored to specific genetic targets, improving treatment outcomes.
4. Enhanced Disease Prevention: By understanding genetic predispositions, personalized medicine through genomics allows for more effective disease prevention strategies and lifestyle modifications.
5. Improved Patient Monitoring: Personalized medicine through genomics facilitates continuous monitoring and adjustment of treatment plans based on the patient’s genetic response to therapies.
The Impact of Personalized Medicine Through Genomics on Healthcare
The integration of personalized medicine through genomics into healthcare systems has transformative potential. It allows physicians to shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to a more individualized model of care. By utilizing genomic information, healthcare providers can predict disease susceptibility, identify optimal treatment protocols, and monitor patient responses with greater precision. This transition not only enhances patient care but also contributes to the sustainability of healthcare systems by reducing unnecessary treatments and improving resource allocation.
Personalized medicine through genomics is redefining the landscape of medical research and development as well. It encourages collaboration between geneticists, clinicians, and policymakers to create robust frameworks for integrating genomic data into clinical practice ethically and responsibly. The development of personalized therapeutics based on genomic insights is leading to groundbreaking treatments and interventions that were previously unimaginable. As knowledge in this domain expands, so does the potential to tackle complex diseases with novel, effective strategies.
Personalized Medicine Through Genomics: A Slang Perspective
1. Personalized medicine through genomics is like getting a custom-made suit, designed just for you. It’s all about precision fit and style.
2. Imagine knowing your body’s cheat code—personalized medicine through genomics gives you that edge.
3. Think of it as your health GPS; personalized medicine through genomics navigates the best route for you.
4. Personalized medicine through genomics is the backstage pass to your own biology.
Read Now : Consulting Healthcare Professionals For Prescriptions
5. It’s like having a personal trainer and dietitian wrapped into one—personalized medicine through genomics optimizes your wellness game.
6. Personalized medicine through genomics means never settling for generic when you can have artisanal healthcare.
7. It takes ‘you do you’ to a whole new level in healthcare.
8. Personalized medicine through genomics is the secret menu of medicine—exclusive and tailored for you.
9. Think of it as personalized playlists, but for your treatments.
10. It’s the difference between buying off-the-rack and bespoke tailoring for your health.
The Role of Data in Personalized Medicine Through Genomics
In the era of personalized medicine through genomics, data plays a crucial, multifaceted role. Gigantic volumes of genetic data can now be generated and analyzed, each piece offering insights into unique personal health narratives. These data guide healthcare providers in making more informed decisions, enhancing the precision of diagnostic and therapeutic processes. Personalized medicine through genomics necessitates robust data infrastructure to support the secure collection, storage, and analysis of genetic information.
Moreover, data sharing and interoperability among healthcare institutions are paramount to fully leverage personalized medicine through genomics. Collaborative data ecosystems can facilitate the identification of patterns and correlations that may be missed in isolated data silos. As we advance into this new era of personalized healthcare, ensuring patient privacy and data security will be critical. Safeguarding genetic information builds trust and encourages individuals to participate in genomic studies, which in turn fuels further advancements.
Future Directions in Personalized Medicine Through Genomics
The future of personalized medicine through genomics is full of possibilities. Continued investment in research and development will drive innovations that improve the precision and accessibility of genomic medicine. Digital technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, will play a pivotal role in analyzing genomic data rapidly and accurately, propelling personalized medicine forward.
A significant future challenge will be integrating personalized medicine through genomics into everyday clinical practice. This will require training healthcare professionals to interpret and apply genomic data effectively. It will also involve creating policy frameworks that support equitable access to personalized healthcare. By addressing these challenges, personalized medicine through genomics will increasingly become a cornerstone of modern medicine, offering hope for improved health outcomes globally.