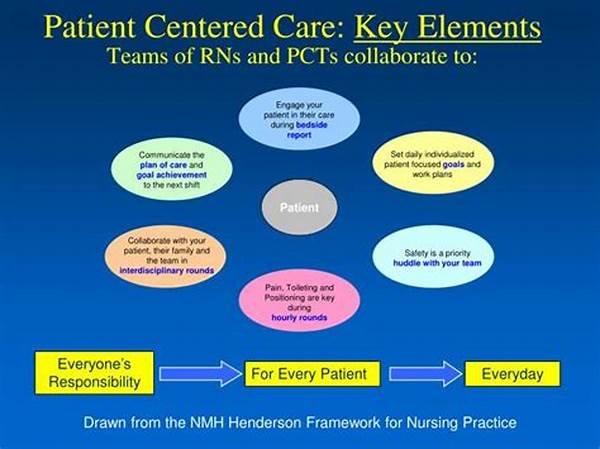
In the contemporary healthcare landscape, an increasing emphasis is placed on delivering care that is not only efficient but also empathetic and responsive to individual patient needs. Patient-centered care models have emerged as a critical framework within this paradigm, aiming to prioritize the personal values, preferences, and needs of the patient. By building on a foundation of trust and communication, these models strive to enhance patient satisfaction, improve healthcare outcomes, and foster a deeper connection between patients and healthcare providers. As healthcare continues to evolve, the importance of patient-centered care becomes ever more pertinent, signaling a shift from traditional, provider-centric models to approaches that truly place the patient at the heart of care.
Read Now : Herbal Prescriptions And Drug Safety
Understanding Patient-Centered Care Models
Patient-centered care models advocate for the holistic consideration of patients’ conditions, including their mental, emotional, and social contexts. These models emphasize active collaboration and open communication between patients and healthcare professionals. Such partnerships ensure that care decisions align with the patients’ preferences and values. Consequently, patient-centered care is designed to become a dynamic, adaptive process. The goal is to provide personalized care that respects and responds to individual patient needs, ultimately leading to enhanced satisfaction and outcomes.
In achieving this, patient-centered care models incorporate elements such as shared decision-making, where patients are empowered to play an active role in their own care journey. Educational resources are provided to inform and guide patients in understanding their conditions and viable treatment options. Moreover, these models seek to reduce the impersonal nature of healthcare encounters by fostering environments where patients feel seen, heard, and respected. The focus is on treating patients not just as a set of symptoms, but as whole individuals, whose unique perspectives and experiences significantly contribute to the healing process.
Key Characteristics of Patient-Centered Care Models
1. Holistic Approach: Patient-centered care models look beyond physical symptoms to consider emotional and social factors that impact patient health.
2. Collaboration: Fostering an active partnership between healthcare providers and patients ensures decisions reflect patient values.
3. Education Empowerment: These models provide resources that enhance patients’ understanding of their health conditions and available treatments.
4. Respect and Dignity: Patients are treated with respect, ensuring their preferences and needs are acknowledged in care planning.
5. Personalization: Care is tailored to the patient’s unique circumstances, promoting a sense of individuality in treatment.
Historical Evolution of Patient-Centered Care Models
Patient-centered care models have evolved considerably over the decades, reflecting broader changes in societal attitudes towards health and wellness. Initially, healthcare was chiefly provider-driven, with patients playing a passive role. Over time, however, growing recognition of the importance of the patient’s voice catalyzed a shift towards more participatory forms of care. This evolution was partly influenced by the rising demand for greater accountability in healthcare and a broader awareness of patients’ rights.
The development of these models can also be attributed to advances in medical research and technology, which have further enabled personalized treatment paradigms. As studies increasingly demonstrated the correlation between patient engagement and improved clinical outcomes, emphasis on patient-centered care deepened. Today, patient-centered care models are integral to healthcare policies worldwide, setting the standard for quality care by recognizing the inherent value of patient autonomy and individual preferences.
Contemporary Applications of Patient-Centered Care Models: A Slang Perspective
1. Keeping it Real: Patient-centered care models make sure healthcare is as authentic as it gets, focusing on real-deal patient needs.
2. No More Cookie-Cutter Care: Each patient’s journey is respected for its uniqueness.
3. Talk the Talk: Communication’s the name of the game; it’s all about keeping that convo open between patients and providers.
4. Squad Goals: With patient-centered care models, it’s about teamwork between patients and providers – working as a unit.
5. Mind Your Vibe: Understanding a patient’s emotional and mental state is just as important as physical symptoms.
Read Now : Targeted Cancer Cell Therapy
6. All About Empowerment: Giving patients the 411 on their health means they’re in charge.
7. Respect Over Everything: No room for disrespect; patient-centered care models put patients’ rights at the forefront.
8. Walk the Walk: It’s not just talk; actions reflect true patient-centered care.
9. Sharing is Caring: Knowledge is power, and sharing it means better decisions for everyone.
10. No Judgement Zone: Every patient’s story is heard without bias; that’s how care should roll.
Impacts of Patient-Centered Care Models on Healthcare Delivery
The widespread adoption of patient-centered care models heralds significant transformation within the healthcare sector. By prioritizing patient autonomy and proactive engagement, these models enhance the quality and effectiveness of healthcare delivery. Patients report higher levels of satisfaction, attributing it to the inclusive nature of care processes that recognize their individual needs and preferences. Particularly, patient-centered care models are associated with improved adherence to treatment plans, reduced hospital readmissions, and higher rates of recovery.
Moreover, these models facilitate a more efficient allocation of healthcare resources. By aligning care with patient needs, unnecessary interventions are minimized, fostering cost-effective healthcare practices. Importantly, patient-centered care models encourage providers to adopt a more empathetic approach, ultimately nurturing more profound patient-provider relationships built on mutual trust and respect. Such dynamics not only improve patient experiences but also enhance the overall healthcare environment, promoting professionalism and accountability across the board.
Challenges in Implementing Patient-Centered Care Models
While the benefits of patient-centered care models are well-documented, their implementation presents several challenges. Foremost, the transition from traditional models necessitates a cultural shift within healthcare institutions, requiring time and persistent effort. Healthcare providers must cultivate the skills necessary for effective communication and shared decision-making, which can demand significant training and adaptation. Furthermore, operational constraints, such as limited time and resources, often hinder the practice of truly personalized care.
Additionally, there is the complexity of measuring outcomes associated with patient-centered care models. Unlike traditional metrics, which primarily focus on clinical results, patient-centered care models demand qualitative evaluations of patient satisfaction and engagement, which can be more challenging to quantify. Despite these challenges, the growing emphasis on holistic, individualized care drives ongoing innovations and solutions, ensuring that patient-centered care models remain a pivotal component of modern healthcare systems.
Summary of Patient-Centered Care Models
Patient-centered care models represent a significant shift in healthcare paradigms, focusing on delivering care that respects and responds to the individual needs of patients. By prioritizing personal values and preferences, these models strive to improve patient satisfaction and healthcare outcomes. Through collaboration and open communication, they empower patients to become active participants in their healthcare journeys. Such participation fosters a sense of autonomy, enhancing the quality and effectiveness of treatments.
Furthermore, patient-centered care models contribute to the creation of a more empathetic healthcare environment. Patients are treated with dignity and respect, ensuring that their voices are heard and valued. This approach leads to stronger patient-provider relationships built on trust, ultimately benefiting both parties. Despite challenges in implementation, the advantages of patient-centered care models underscore their fundamental role in contemporary healthcare, advocating for practices that truly place patients at the heart of care.