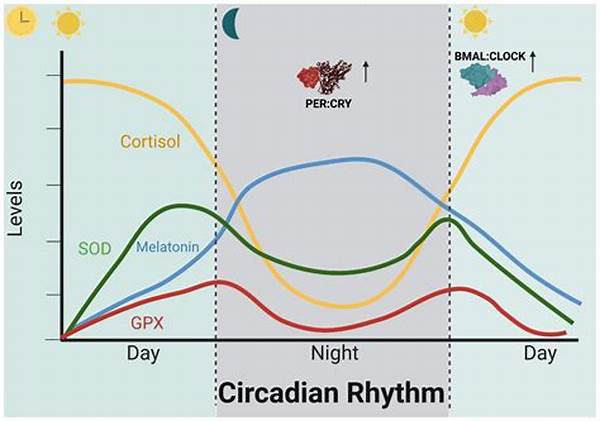
The circadian rhythm, an intrinsic timekeeping system, orchestrates a wide array of physiological processes, aligning them with the 24-hour day-night cycle. Pharmacological interventions can significantly modulate this rhythm, offering therapeutic potential for various disorders. Understanding the intricacies of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm is crucial, as these effects can influence a plethora of bodily functions, including sleep patterns, metabolism, and hormone release. This exploration will delve into how pharmacological agents impact the circadian system, offering insights into potential therapeutic applications and considerations.
Read Now : Stress Relief With Essential Oils
The Interplay Between Pharmacology and Circadian Regulation
Pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm can manifest in numerous ways, affecting not only sleep but also overall health. Pharmaceutical agents can either reinforce the circadian rhythm, acting as synchronizers, or disrupt it, leading to potential health complications. For instance, certain medications that promote wakefulness can suppress melatonin production, shifting the circadian rhythm and potentially causing disorders such as insomnia or delayed sleep phase syndrome. Conversely, some pharmacological treatments are designed explicitly to rectify circadian misalignments by manipulating neurotransmitters that are central to circadian regulation. These effects underline the significance of timing in pharmacotherapy, where the administration of drugs can be optimized based on the body’s circadian rhythm to improve efficacy and reduce side effects. Consequently, understanding and harnessing pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm can greatly enhance therapeutic outcomes for various chronobiological disorders.
Furthermore, the exploration of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm includes examining the role of chronotherapeutics, a field dedicated to optimizing drug delivery timing. Through this lens, medications can be administered in alignment with the body’s natural rhythms, increasing their effectiveness and minimizing adverse reactions. This is particularly pertinent in conditions such as hypertension, where blood pressure follows a circadian pattern. Tailoring medication schedules according to these natural variations can lead to more effective management of the condition. Ultimately, the pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm present a promising avenue for improving patient care by aligning therapeutic interventions with the body’s intrinsic timekeeping mechanisms.
Comprehensive Insights into Pharmacological Influences
1. Pharmacological Adjustments: The circadian rhythm can be both positively and negatively influenced by pharmaceuticals, altering sleep and performance. Pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm need precise management to prevent adaptation and potential desynchronization.
2. Chronotherapy Application: By aligning drug delivery with the circadian cycle, pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm can be harnessed for enhanced treatment efficacy, providing a strategic advantage in clinical settings.
3. Melatonin Modulation: Some drugs have the potential to alter melatonin pathways, illustrating significant pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm. This can be pivotal for treatments involving sleep disorders or managing jetlag.
4. Sleep-Wake Cycle Considerations: Pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm often target the sleep-wake cycle, offering therapeutic options for sleep phase disorders through agonists and antagonists of key neurotransmitters.
5. Metabolic Impacts: Understanding pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm is equally important for metabolic processes. Certain drugs might impact glucose regulation and lipid metabolism, necessitating careful consideration of dosing schedules.
Delineating Pharmacological Effects on Circadian Rhythms
The efficacy of pharmacological interventions is profoundly intertwined with the understanding of biological rhythms. The circadian system manages diverse physiological activities, implicating numerous biological pathways that respond to pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm. In particular, the synchronization between pharmacokinetics, the movement of drugs within the body, and pharmacodynamics, the drug’s effects on the body, can be optimized in accordance with these rhythms. As drug actions may elicit varied responses at different circadian phases, tailoring pharmacological regimens with precise circadian alignment can enhance therapeutic interventions while minimizing adverse effects.
Researchers have increasingly recognized the need for data-driven approaches to ascertain the optimal timing for drug administration. The study of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm encompasses a range of investigative methodologies, from clinical trials to computational modeling, aiming to fine-tune treatment protocols. By leveraging cutting-edge technologies and a deep understanding of circadian biology, healthcare professionals can devise innovative strategies to integrate circadian principles into individualized treatment plans. This approach fosters improved therapeutic precision, maximizing the beneficial outcomes of pharmacological interventions.
Evaluating Circadian Pharmacology: A Modern Perspective
Understanding pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm is pivotal for the development of modern pharmaceuticals and their clinical applications. By examining the interplay between drug mechanisms and the body’s inherent clock, researchers can develop targeted treatment strategies. Drug development processes now incorporate chronopharmacology, which emphasizes the alignment of drug actions with the circadian phases to maximize efficacy and minimize adverse reactions. This approach represents a transformation in how we perceive and address physiological disruptions through pharmacological means.
Read Now : Enhancing Drug Action With Precise Scheduling
As the relevance of circadian rhythm in health and disease becomes increasingly apparent, pharmacology is at the forefront of addressing these challenges. Pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm are central to the development of novel treatments for disorders traditionally considered difficult to manage, such as certain sleep disorders, mood disorders, and metabolic conditions. By continuing to explore these effects, the medical community is better positioned to revolutionize therapeutic approaches, setting the stage for more effective and tailored interventions in healthcare.
Advancing Research in Circadian Pharmacology
The advancement of research into pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm is crucial for understanding how medications can be optimized for circadian alignment. Given the circadian rhythm’s regulatory role in various bodily processes, its interaction with pharmaceutical agents influences the clinical outcomes of numerous treatments. Moreover, exploratory studies have revealed that disruption in the circadian rhythm can lead to increased susceptibility to disease, emphasizing the need for circadian-aligned pharmacological interventions.
Recent advances in chronobiology highlight the significance of circadian biology in drug response. With greater insights into molecular pathways and genetic factors influencing circadian regulation, researchers can develop interventions that align with the circadian rhythm, thereby enhancing clinical outcomes. The exploration of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm not only holds the potential for better managing diseases but also contributes to a broader understanding of biological systems. As scientific inquiry progresses, the partnership between pharmacology and circadian biology continues to grow, offering promising avenues for the future of medicine.
The Role of Pharmacological Agents in Circadian Correction
Pharmacological interventions targeting the circadian rhythm have gained traction due to their potential in addressing disorders with a significant rhythmic component. The exploration of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm encompasses various mechanisms, from receptor agonists that mimic endogenous signals to antagonists that inhibit disruptive pathways. These interventions offer novel opportunities for aligning treatments with the body’s natural rhythms.
Further, the potential for using pharmacological agents to correct circadian misalignments, such as those found in shift work syndrome or jet lag, showcases their utility in modern therapeutic contexts. By focusing on the temporal dynamics of drug action, researchers and clinicians can fine-tune therapies to address the synchronization of internal clocks. The broader understanding of pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm exemplifies a significant shift towards personalized medicine, where treatments are not only patient-specific but also time-specific, maximizing the potential for successful outcomes.
Harnessing Pharmacological Effects on Circadian Rhythm: Future Directions
As the scientific community pursues further research into the pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm, it becomes increasingly evident that this area holds considerable promise for enhancing medical practice. By delving deeper into the interplay between pharmacological interventions and circadian biology, researchers hope to uncover more sophisticated ways to manipulate biological rhythms beneficially. Efforts in this domain are likely to yield therapeutic breakthroughs, contributing to a broader understanding of human health and disease management.
Ultimately, refining our approaches to pharmacological effects on circadian rhythm offers a pathway to improving health outcomes globally. By ensuring medications align with the body’s natural cycles, healthcare providers can enhance treatment modalities and patient experiences. This harmonization of pharmacology and chronobiology represents a forward-thinking approach to modern medicine, paving the way for innovations that prioritize both biological science and patient care.