In the realm of modern healthcare, preventative health measures in medicine play a pivotal role in enhancing patient outcomes and optimizing the efficiency of healthcare systems. These measures encompass a wide array of strategies aimed at averting the onset of diseases, minimizing risks, and promoting overall wellbeing. Understanding and implementing preventative health measures is essential for healthcare providers, policymakers, and individuals alike. This article delves into the significance, methodologies, and outcomes associated with preventative health measures in medicine, highlighting how these practices can lead to a healthier society.
Read Now : Prescription Medication For Hospitals
Importance of Preventative Health Measures
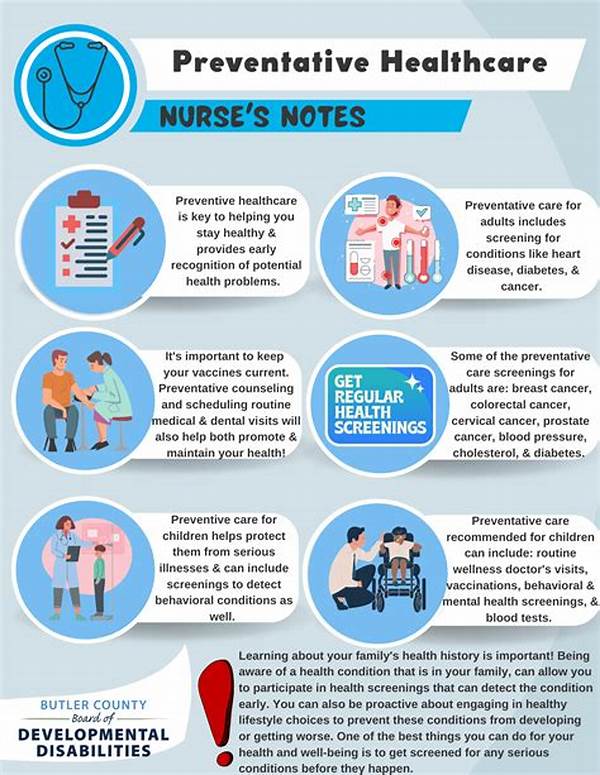
Preventative health measures in medicine represent a paradigm shift from reactive to proactive healthcare. This approach focuses on identifying risk factors and employing strategies to mitigate these risks before they can result in adverse health outcomes. Such measures include vaccinations, screenings, lifestyle modifications, and health education. By addressing potential health issues at an early stage, preventative health measures can significantly reduce the incidence of chronic illnesses, thereby reducing healthcare costs and enhancing quality of life. The emphasis on prevention also promotes health equity, ensuring that diverse populations have access to necessary interventions and resources. In a world where healthcare resources are often strained, preventative health measures in medicine provide a sustainable model to maintain public health and prevent the overwhelming burden of disease.
Key Components of Preventative Health Measures
1. Vaccination Programs: Vaccinations are fundamental preventative health measures in medicine, providing immunity and reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
2. Routine Screenings: Regular health screenings allow for early detection of diseases, which can be pivotal in effective management and treatment.
3. Lifestyle Modifications: Encouraging healthy lifestyle choices, such as balanced diets and regular exercise, greatly contributes to the prevention of numerous health conditions.
4. Health Education: Educating the public on healthy practices and awareness about diseases empowers individuals to make informed health decisions.
5. Risk Factor Assessment: Identifying and addressing individual risk factors help tailor preventative strategies to meet specific patient needs, maximizing efficacy.
Strategies for Implementing Preventative Health Measures
Implementing preventative health measures in medicine requires a comprehensive and multifaceted approach. Healthcare providers must collaborate with policymakers, community leaders, and patients to establish and promote prevention-focused policies. Public health campaigns can be instrumental in raising awareness and encouraging community participation in preventative screenings and educational programs. Additionally, integrating technology into healthcare practices—such as electronic health records and telemedicine—can improve accessibility and adherence to preventative measures. For instance, reminders for vaccinations or screenings can be automated to ensure that individuals do not miss crucial appointments. Central to these strategies is the need for culturally sensitive practices that cater to the diverse needs of different communities, ensuring that preventative health measures in medicine are both inclusive and effective.
Read Now : Risk Of Herbal Drug Interactions
The Impact of Preventative Health Measures
The impact of preventative health measures in medicine extends beyond individual health, influencing broader societal outcomes. By reducing the prevalence of diseases, preventative measures alleviate pressure on healthcare systems, allowing for optimal allocation of resources. This results in economic benefits, as healthier populations lead to increased productivity and reduced absenteeism in the workplace. Furthermore, fostering a culture of prevention cultivates a more informed public that actively engages in maintaining health, creating a ripple effect that benefits future generations. As nations worldwide grapple with the challenges posed by aging populations and emerging health threats, preventative health measures in medicine offer a sustainable solution to confronting these issues, promoting a healthier future for all.
Preventative Health Measures in Pediatrics
Pediatric care offers a unique opportunity to implement preventative health measures in medicine from an early age. Initiating these measures during childhood, such as routine immunizations and developmental screenings, ensures a foundation for lifelong health. By ingraining healthy habits in children and their caregivers, healthcare providers can significantly influence health trajectories. Preventative strategies in pediatrics are not limited to physical health but also encompass mental and emotional wellbeing. Early intervention and support can enhance resilience in children, equipping them to navigate life’s challenges. Pediatric preventative health measures exemplify the long-term benefits of a prevention-focused approach and underscore the crucial role of healthcare providers in fostering a healthier future generation.
Barriers to Effective Preventative Health Measures
Despite their clear advantages, the implementation of preventative health measures in medicine can face substantial barriers. Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty and lack of access to healthcare services, can impede individuals’ ability to engage in prevention programs. Additionally, cultural differences and language barriers may prevent certain communities from fully participating in preventative initiatives. Addressing these disparities requires targeted efforts to ensure equitable access and culturally competent care. Research and policy development must prioritize overcoming these obstacles, leveraging community partnerships and outreach to bridge gaps in care. Understanding these challenges and actively working to address them is crucial for the successful deployment of preventative health measures globally.
Conclusion
In conclusion, preventative health measures in medicine are indispensable components of modern healthcare systems. They offer a proactive approach to managing health risks, promoting wellness, and improving population health outcomes. By emphasizing prevention, stakeholders can reduce healthcare costs, enhance quality of life, and ensure accessible care for all. The success of preventative health measures relies on collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, policymakers, and communities. Only through such integrated approaches can the full potential of preventative health measures in medicine be realized, paving the way for a healthier and more sustainable future.