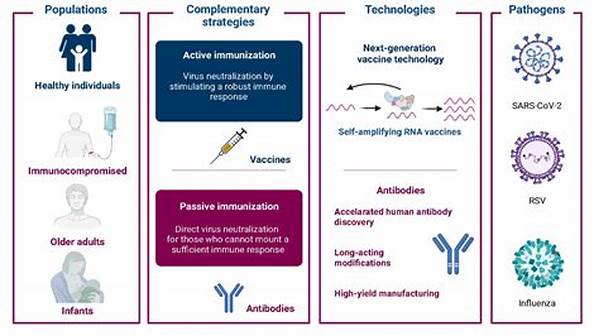
Importance and Implementation of the Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
The immunization disease eradication strategy represents a cornerstone of public health efforts globally, serving as a critical tool to eliminate diseases that have plagued humanity for centuries. This strategy is essential not only for the immediate reduction in disease incidence but also for the long-term benefits associated with disease eradication. The global eradication of smallpox in the 20th century stands as a testament to what the immunization disease eradication strategy can achieve. By implementing this strategy, health organizations aim to provide individuals, especially in vulnerable populations, with access to vaccines that grant immunity against preventable diseases. Achieving high immunization coverage is imperative to ensure the success of these efforts, as it significantly reduces the transmission rates of infectious diseases, thus protecting communities at large.
Read Now : Immediate Medical Intervention Teams
Financial planning is another critical aspect of the immunization disease eradication strategy. Governments and non-governmental organizations must allocate substantial budgets to support vaccine procurement, distribution, and administration. This involves investing in health infrastructures, such as cold chain systems for vaccine storage and transport, to maintain vaccine efficacy. Furthermore, continuous monitoring and evaluation processes are integrated into the strategy to assess vaccine coverage and identify any gaps in immunization services. Such measures ensure that the immunization disease eradication strategy is adapted to address emerging challenges, including new disease outbreaks or vaccine hesitancy within communities.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in the successful implementation of the immunization disease eradication strategy. They are responsible for educating the public about the importance of vaccination and dispelling myths and misinformation that could hinder vaccine uptake. Training healthcare workers on the latest immunization guidelines and strategies fosters a more effective and efficient delivery of vaccination programs. Collaborative efforts between international health bodies, governments, and local communities are vital in addressing disparities in vaccine access and distribution, ultimately steering global health systems toward their goal of disease eradication.
Challenges in the Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
1. Vaccine hesitancy presents a significant obstacle to the immunization disease eradication strategy, as misinformation and skepticism can lead to decreased vaccine uptake, undermining public health efforts.
2. Financial constraints often limit the ability of countries to fully implement the immunization disease eradication strategy, impacting vaccine availability and healthcare infrastructure development.
3. Geographical barriers pose a serious challenge to the immunization disease eradication strategy, as remote areas may lack access to vaccines due to difficult terrain and insufficient healthcare facilities.
4. Political instability can disrupt the immunization disease eradication strategy by causing interruptions in vaccine supply chains and creating unsafe environments for healthcare professionals.
5. Emerging diseases require constant adaptation of the immunization disease eradication strategy, necessitating the development of new vaccines and strategies to address unforeseen health threats.
The Role of Global Partnerships in Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
The immunization disease eradication strategy is greatly enhanced by the collaboration between various global entities, including international health organizations, governments, and non-profit organizations. These partnerships are pivotal to orchestrating a unified response to tackle diseases that cross borders and impact populations worldwide. By sharing resources, expertise, and technology, global partnerships can bolster the effectiveness and reach of immunization campaigns, making vaccines more accessible even in the most remote or under-resourced regions.
Financial backing and resource mobilization from affluent nations and global health funds enable the distribution of vaccines to low-income countries, reinforcing the immunization disease eradication strategy. These partnerships also facilitate research and development of new vaccines and the enhancement of existing ones, ensuring a comprehensive arsenal against evolving pathogens. Knowledge exchange and capacity-building initiatives further strengthen the ability of national healthcare systems to execute immunization plans efficiently, with particular focus on training healthcare workers and developing robust surveillance systems to monitor the progress and challenges of eradication efforts.
Public-private partnerships further contribute to the immunization disease eradication strategy by involving pharmaceutical companies in the production and distribution processes. Through these collaborations, vaccines can be produced and supplied at an accelerated rate, meeting the demands of global immunization requirements. Ultimately, the unified approach of global partnerships fosters a resilient framework for combatting vaccine-preventable diseases, working towards a future where diseases such as polio and measles are entirely eradicated, safeguarding health for generations to come.
Pop Culture’s Take on Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
1. You know, immunization’s like that team effort in volleyball – everyone’s gotta hit their spot for the win. The immunization disease eradication strategy is about everyone teaming up to kick diseases out!
2. Think of vaccines as those magical potions in video games. The immunization disease eradication strategy is making sure everyone gets their potion to fight the boss – aka the disease.
3. Remember in school, getting that gold star for perfect attendance? The immunization disease eradication strategy is like striving for that gold star, except it’s about having no more diseases showing up.
4. Immunization disease eradication strategy is like a societal Spotify playlist; everyone’s got their tune (vaccine) that gets diseases to skip out on the charts permanently.
5. Picture diseases as unwelcome party crashers. The immunization disease eradication strategy is the VIP guest list; if you’re vaccinated, you’re in, and diseases are out.
6. Ever had that friend who organizes group texts to keep everyone on the same page? The immunization disease eradication strategy is like that, but for ensuring health info is spot on.
Read Now : Implementation Strategies For Guidelines
7. Like deleting old files from your phone to make space, the immunization disease eradication strategy clears out diseases, making room for healthier tomorrows.
8. Immunization disease eradication strategy’s like that epic internet meme; everyone shares it, spreading health vibes and high-fiving globally over less disease.
9. Vaccines, in the scope of immunization disease eradication strategy, are the Jedi knights of health, lightsabering diseases out of our galaxy for good.
10. Immunization disease eradication strategy is the superhero storyline – each vaccine dose is a mighty punch toward vanishing villains (diseases) once and for all.
Evaluating Success Metrics in the Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
Evaluating the success of the immunization disease eradication strategy requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses a multitude of indicators. One key metric is the reduction in incidence rates of specific diseases targeted by the eradication program. A decline in these rates directly signals the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns and the overall robustness of the strategy. It is essential to track both immediate and long-term impacts to ensure sustained success, considering potential fluctuations due to emerging challenges such as pathogen mutations or regional outbreaks.
Another crucial measure involves quantifying vaccine coverage rates, particularly in high-risk and under-vaccinated populations. Achieving and maintaining a high coverage percentage ensures the establishment of herd immunity, a pivotal aspect of the immunization disease eradication strategy. Monitoring these rates necessitates sophisticated tracking systems and accurate data collection, often involving electronic health records and national immunization registries. Moreover, evaluating the success of the strategy also involves assessing public perception and engagement with vaccination programs, understanding factors that influence vaccine acceptance, and tailoring communication strategies to address hesitancy effectively.
The immunization disease eradication strategy’s success is further evaluated through economic analyses that highlight cost-effectiveness and return on investment. Reducing the prevalence of vaccine-preventable diseases translates to substantial healthcare savings, as fewer resources are required for treatment and management of outbreaks. Additionally, the broader socio-economic benefits, such as improved quality of life and increased productivity due to healthier populations, are critical components in assessing the overall success of these initiatives. Through comprehensive evaluation metrics, stakeholders can make informed decisions, refine strategies, and prioritize resources effectively to enhance the global impact of disease eradication efforts.
Long-Term Goals of the Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
The long-term goals of the immunization disease eradication strategy revolve around creating a world where vaccine-preventable diseases are no longer a public health threat. Central to these goals is the complete elimination of diseases such as polio and measles through sustained vaccination efforts and robust surveillance systems. Achieving these outcomes requires multi-faceted approaches, including strengthening healthcare infrastructure and enhancing global cooperation to support equitable access to vaccines.
Moreover, the immunization disease eradication strategy aims to foster a culture of prevention among all populations, prioritizing education and awareness about the vital role vaccines play in individual and public health. This involves comprehensive outreach programs targeting schools, communities, and workplaces to embed the principles of immunization into the fabric of societal norms. A key aspect of achieving long-term goals is addressing vaccine hesitancy by building trust between healthcare providers and patients, leveraging evidence-based communication to debunk myths and misinformation.
Furthermore, sustainable financing and policy-making underpin the long-term success of the immunization disease eradication strategy. Governments and international partners must commit to continued funding and strategic planning that anticipate future challenges, including emerging infectious diseases. Enhanced research and development initiatives are also integral, ensuring the availability of innovative vaccines that can respond to evolving pathogen landscapes. By aligning these strategic priorities, the global community can move closer to a future where the threat of vaccine-preventable diseases is a relic of the past, safeguarding generations to come.
Summary of the Immunization Disease Eradication Strategy
The immunization disease eradication strategy represents a comprehensive and multi-dimensional approach to reducing and ultimately eliminating vaccine-preventable diseases that pose significant public health challenges. Through heightened vaccination coverage, the strategy aims to curtail the transmission and prevalence of diseases such as polio, measles, and others, leveraging vaccination campaigns as critical interventions. Central to this strategy is the establishment of robust monitoring systems to evaluate vaccine coverage and disease incidence rates, enabling health organizations to track progress and address potential gaps in service delivery promptly.
Collaboration among international health organizations, governments, and non-profit entities is vital to achieving the objectives of the immunization disease eradication strategy. By pooling resources, expertise, and technologies, these alliances enhance the capacity to provide equitable access to vaccines globally, even in the most remote or conflict-ridden regions. Public-private partnerships further contribute by streamlining the production and distribution of vaccines, ensuring that immunization efforts meet the demands of diverse populations effectively.
In addressing challenges such as vaccine hesitancy, financial constraints, and geopolitics, the immunization disease eradication strategy emphasizes educational outreach and community engagement to foster trust and confidence in vaccination programs. Long-term goals focus on establishing prevention-oriented societies where the historic burden of vaccine-preventable illnesses is significantly reduced or eradicated. With sustained commitment, adaptation to emerging challenges, and reinforcement of healthcare systems, the immunization disease eradication strategy charts a course toward a healthier, disease-free world.