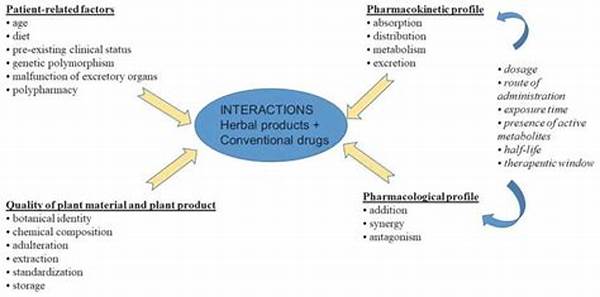
In the realm of healthcare, the incorporation of herbal medicines into treatment regimens has gained considerable popularity due to their natural derivation and perceived health benefits. However, despite their widespread use, there remains a significant concern regarding the risk of herbal drug interactions. This issue is of paramount importance as it affects patient safety and treatment efficacy, necessitating astute awareness and understanding among healthcare professionals.
Read Now : Individualized Treatment With Herbs And Drugs
Understanding the Risk of Herbal Drug Interactions
Herbal medicines, while beneficial in many respects, are not without potential complications. The risk of herbal drug interactions emerges when these natural products are consumed alongside conventional pharmaceuticals. Herbal constituents can influence the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of prescription drugs, leading to either diminished therapeutic outcomes or enhanced toxicity. For instance, St. John’s Wort is known to induce cytochrome P450 enzymes, which can significantly reduce the efficacy of certain anticancer drugs and oral contraceptives. Furthermore, ginkgo biloba has been associated with increased bleeding risks when taken with anticoagulants. These interactions underscore the necessity for comprehensive patient education and meticulous medication history assessments. Healthcare providers must diligently inform patients of the potential risks and carefully review any herbal products being used concurrently with prescription medications.
Common Interactions and Their Impacts
1. St. John’s Wort and Antidepressants: The risk of herbal drug interactions is highly evident when St. John’s Wort is paired with antidepressants, potentially leading to serotonin syndrome, a life-threatening condition.
2. Ginkgo Biloba and Anticoagulants: The concurrent use of Ginkgo Biloba and anticoagulants poses a notable risk of herbal drug interactions, increasing the likelihood of bleeding complications.
3. Garlic and Antiplatelet Drugs: Garlic supplements can heighten the risk of herbal drug interactions by augmenting the effects of antiplatelet drugs and raising bleeding proclivity.
4. Ginseng and Warfarin: A prominent risk of herbal drug interactions exists between ginseng and warfarin as ginseng may reduce warfarin’s anticoagulation efficacy.
5. Echinacea and Immunosuppressants: Echinacea can interfere with immunosuppressants, highlighting the risk of herbal drug interactions by potentially diminishing the immune-suppressing effects crucial for transplant patients.
Potential Risks and Precautionary Measures
The risk of herbal drug interactions is a double-edged sword that calls for considerable vigilance and precautionary measures. As herbal preparations are often perceived as innocuous due to their natural origin, the tendency to overlook their potential to interact adversely with pharmaceutical agents is commonplace. Patients frequently self-administer herbal products without prior consultation with healthcare professionals, thereby inadvertently increasing the risk of adverse interactions. Thus, the onus lies with healthcare providers to actively inquire about herbal use during patient assessments and to offer informed guidance regarding potential interactions. Collaboration between practitioners and patients is essential to minimize risks through educating patients on safe practices and fostering open communication about all substances being consumed.
Read Now : Customized Herbal Remedy Plans
Addressing the Risks with Careful Monitoring
To adequately address the risk of herbal drug interactions, implementing robust monitoring frameworks is indispensable. Healthcare professionals should undertake detailed patient histories encompassing all medications, including over-the-counter and herbal products. Furthermore, fostering an environment where patients feel comfortable discussing their use of herbal remedies without fear of judgment is imperative. This dialogue ensures that healthcare providers can deliver tailored advice aimed at mitigating potential risks. By promoting a culture of transparency and vigilance, the healthcare system can adeptly manage the risk of herbal drug interactions and safeguard patient well-being, thereby optimizing therapeutic outcomes.
A Comprehensive Exploration of Clinically Relevant Interactions
The clinical landscape provides myriad instances where the risk of herbal drug interactions poses a considerable challenge to achieving safe and effective treatment regimens. One significant interaction arises with the use of St. John’s Wort, an herbal remedy frequently employed for its antidepressant properties. However, St. John’s Wort is potent in affecting drug metabolism through the induction of cytochrome P450 enzymes, subsequently reducing plasma levels of various medications and compromising their clinical efficacy. Moreover, ginkgo biloba, a prominent herbal supplement praised for its cognitive-enhancement capabilities, exacerbates bleeding risk when combined with anticoagulants such as warfarin, thus illustrating the paramount necessity of meticulous coordination between herbal and pharmaceutical therapies.
Effective management of the risk of herbal drug interactions requires a multifaceted approach. Initially, healthcare providers must prioritize obtaining thorough medication histories during patient consultations to identify concurrent use of herbal and pharmaceutical products. Follow-up with patient education focused on highlighting potential interaction risks ensures that patients are better equipped to make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, healthcare professionals should remain updated on emerging evidence regarding novel interactions. By instituting rigorous medication management protocols and fostering interdisciplinary communication, healthcare institutions can effectively minimize the potential harm posed by such interactions.
Concluding Remarks on Mitigating Risks
In summary, while herbal medicines present an attractive therapeutic option for many individuals, the risk of herbal drug interactions cannot be understated and demands careful attention within healthcare practices. It is incumbent upon healthcare providers to engage in comprehensive patient education endeavors, ensuring that individuals are aware of potential interactions when integrating herbal supplements into their treatment plans. Establishing open dialogues with patients regarding all substances consumed allows for strategic intervention to preclude adverse outcomes. Furthermore, embracing continuous professional development and staying abreast of pertinent research findings are essential for the proactive management of these risks. Together, these approaches enable healthcare practitioners to provide safe, effective, and informed patient care that navigates the complexities of integrating herbal and conventional medicine modalities.