Hypertension, commonly referred to as high blood pressure, is a prevalent medical condition that poses serious health risks if left untreated. The management of hypertension is critical for preventing complications such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney failure. One of the primary approaches to managing hypertension involves the use of pharmacological interventions, specifically effective drugs for hypertension management. These medications play a crucial role in lowering blood pressure levels and maintaining cardiovascular health.
Read Now : Efficient Home Medicine Organization
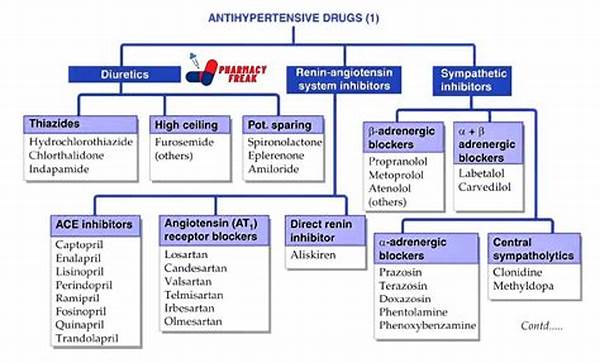
Classes of Antihypertensive Drugs
Effective drugs for hypertension management can be categorized into several classes, each working through different mechanisms to achieve the desired effect. The primary classes of antihypertensive drugs include diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and calcium channel blockers. Diuretics help reduce the volume of blood, thus lowering blood pressure, while beta-blockers decrease heart rate and the force of contraction, reducing cardiac output. ACE inhibitors and ARBs work by preventing the constriction of blood vessels, whereas calcium channel blockers relax blood vessel walls. The choice of an appropriate antihypertensive medication depends on the patient’s overall health, the presence of other conditions, and specific response to the medication. Thus, an understanding of these drug classes is essential for devising an optimal treatment strategy in effective drugs for hypertension management.
Mechanisms of Action
1. Diuretics aid in effective drugs for hypertension management by promoting sodium and water excretion, reducing intravascular volume.
2. Beta-blockers contribute to blood pressure reduction by decreasing sympathetic nervous system activity.
3. ACE inhibitors hinder the production of angiotensin, leading to vasodilation.
4. ARBs block angiotensin receptors, preventing vasoconstriction.
5. Calcium channel blockers interfere with calcium entry into vascular smooth muscle, promoting relaxation and lowering blood pressure.
Current Research and Developments
Ongoing research in the field of hypertension management continually evolves, with an emphasis on discovering novel therapeutic agents and improving the efficacy of existing medications. Recent studies explore the genetic factors influencing individual responses to antihypertensive drugs, paving the way for personalized medicine approaches. Furthermore, there is a growing interest in combining pharmacological treatments with lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity, to enhance the overall efficacy of hypertension management. Harnessing data from clinical trials and real-world studies, researchers aim to refine the options available in effective drugs for hypertension management, thereby addressing both the physiological and behavioral aspects of the condition.
Read Now : Relaxation Through Controlled Breathing
The Role of Lifestyle in Drug Efficacy
Effective drugs for hypertension management are most beneficial when used in conjunction with lifestyle modifications. Patients are encouraged to adopt heart-healthy habits, such as reducing dietary sodium intake, engaging in regular physical exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol consumption. These lifestyle adjustments complement the pharmacological effects of antihypertensive medications, facilitating better control of blood pressure levels. A multidisciplinary approach that integrates lifestyle changes with pharmacotherapy not only optimizes treatment outcomes but also contributes to the patient’s overall well-being. As such, healthcare providers emphasize the significance of a holistic plan that incorporates both medication adherence and lifestyle adaptations to achieve optimal results in effective drugs for hypertension management.
Personalized Hypertension Management
Personalized medicine is at the forefront of effective drugs for hypertension management. This approach tailors treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, such as genetic profiles, comorbidities, and drug tolerances. Advances in pharmacogenomics allow for the identification of genetic markers that predict patient response to specific medications, thus enabling the selection of the most effective therapeutic agent. Consequently, personalized hypertension management reduces the trial-and-error approach often associated with prescribing antihypertensive drugs and enhances patient outcomes through precision treatment strategies.
Potential Adverse Effects
While effective drugs for hypertension management significantly lower blood pressure, it is crucial to monitor for potential adverse effects. Common side effects include dizziness, fatigue, and electrolyte imbalances, with the risk varying depending on the specific medication class. A thorough understanding of a patient’s medical history and close monitoring of drug efficacy and tolerability help mitigate these risks. Healthcare providers must communicate openly with patients about potential side effects to ensure adherence to treatment regimens and adjust therapies as needed to maintain both safety and efficacy in hypertension management.
Summary of Hypertension Drug Management
The implementation of effective drugs for hypertension management largely depends on a comprehensive understanding of pharmacological mechanisms and patient-specific factors. A tailored approach, integrating both drug therapy and lifestyle modification, is paramount in achieving the desired therapeutic goal of sustained blood pressure control. As research advances, the pursuit of personalized medicine continues to evolve, underpinning the potential for more precise, individualized treatment plans. Engaging patients in their care process, educating them about the importance of adherence to prescribed medications, and fostering lifestyle changes can significantly enhance the success of hypertension management strategies, ultimately reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications and improving quality of life.