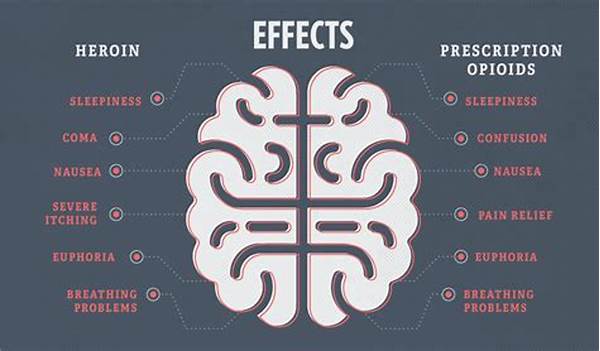
The combination of different prescription medications is an increasingly common practice due to the prevalence of multiple health conditions in patients worldwide. While it may offer therapeutic advantages, it also carries potential risks that cannot be ignored. Understanding the consequences of combining different prescriptions is crucial for healthcare providers and patients alike to ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks.
Read Now : Effective Plant Therapies For Anxiety
Understanding Drug Interactions
Combining various prescription drugs can lead to drug interactions, which are changes in a drug’s effects due to the presence of other substances. These interactions can heighten the effects of drugs, reduce efficacy, or lead to unexpected side effects, representing the potential consequences of combining different prescriptions. Drug interactions are influenced by various factors, including the patient’s age, weight, and overall health status. For example, older adults, who might be on numerous medications, are at a higher risk of experiencing adverse interactions. Moreover, certain medications might interact with over-the-counter drugs or dietary supplements, complicating treatment outcomes further. It is essential to monitor the patient’s response to combined prescriptions closely and adjust treatments as necessary to mitigate the negative consequences of combining different prescriptions.
Types of Risk When Combining Medications
1. Therapeutic Duplication: The consequences of combining different prescriptions include the risk of therapeutic duplication where similar medications increase the risk of overdose.
2. Increased Side Effects: Combining drugs can amplify side effects, leading to discomfort or serious health issues, highlighting the importance of understanding the consequences of combining different prescriptions.
3. Reduced Drug Efficacy: Some drugs might negate each other’s effectiveness, thus failing to treat the condition and emphasizing one of the potential consequences of combining different prescriptions.
4. Dangerous Interactions: The consequences of combining different prescriptions can result in harmful drug interactions that might endanger the patient’s life.
5. Complexity in Management: Managing multiple medications becomes challenging, increasing the risk of non-adherence, showcasing another of the consequences of combining different prescriptions.
Strategies for Safe Medication Management
To mitigate the consequences of combining different prescriptions, healthcare professionals must conduct thorough patient assessments. Evaluating a patient’s complete medication regimen, including both prescription and over-the-counter drugs, can help identify potential risks. Communication is key; patients should be encouraged to disclose all medications, supplements, and herbal products they are using. This transparency allows for the careful selection of medications and the avoidance of combinations that could lead to adverse interactions. Additionally, pharmacists play a crucial role in monitoring prescriptions and advising both healthcare providers and patients on possible drug interactions that could manifest as the consequences of combining different prescriptions. Education on safely managing polypharmacy can empower patients to adhere to their medication regimens more diligently.
Read Now : Anxiety-easing Tea With Natural Herbs
Risks of Self-Medicating
Self-medicating can significantly amplify the consequences of combining different prescriptions. When individuals choose to take multiple medications without professional guidance, they run the risk of inadvertently mixing drugs that can cause harmful interactions. The lack of professional oversight might lead to incorrect dosages or missing vital warnings about potential adverse effects. Growing dependency on self-medication practices, driven by easy access to over-the-counter drugs and information from non-professional sources, further compounds these risks. Finally, as patients might not be fully informed about the consequences of combining different prescriptions, there is a significant possibility of exacerbating existing health issues, rather than resolving them.
The Role of Electronic Health Records
The use of Electronic Health Records (EHR) significantly aids in reducing the consequences of combining different prescriptions. EHRs provide comprehensive patient medication histories, enabling healthcare providers to spot potential drug interactions swiftly. This technology facilitates better communication among healthcare teams, ensuring all prescribed medications are accounted for. Consequently, patients benefit from safer and more effective treatment regimens. EHR systems often include alert functions that trigger warnings about potential adverse drug interactions, assisting in preventing the negative consequences of combining different prescriptions. This emphasizes the importance of adopting comprehensive technological solutions in modern healthcare practices to safeguard patients’ well-being.
Patient Education and Awareness
Educating patients about their medications is vital in minimizing the consequences of combining different prescriptions. When patients understand how each of their medications works, they are better equipped to recognize potential side effects or interactions. Healthcare providers should ensure that patients receive comprehensive information about each medication’s purpose, dosage, and potential interactions. By fostering an environment of open communication and trust, patients are more likely to ask questions and discuss concerns about their treatment plans. Ultimately, informed patients who actively participate in their healthcare decisions contribute significantly to preventing adverse consequences of combining different prescriptions.
Summary
The consequences of combining different prescriptions underscore the need for vigilant medication management and patient education. Interactions between medications can result in a spectrum of issues, ranging from increased side effects to reduced therapeutic efficacy. Healthcare providers must be proactive in evaluating and communicating with patients about their complete medication regimen, including non-prescription drugs and supplements. Leveraging technology such as Electronic Health Records can aid in identifying and preventing potential negative interactions, thus averting the adverse consequences of combining different prescriptions. Through comprehensive patient education, individuals are empowered to engage with their healthcare decisions actively, minimizing risks and enhancing health outcomes.