Hypertension, more commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent condition that often requires medical intervention to manage effectively. The treatment of hypertension is crucial as it can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other serious health issues. A variety of medications known as antihypertensive drugs are utilized in clinical practice to control high blood pressure. Among these are several popular antihypertensive drugs that are widely prescribed due to their effectiveness and reliability. This article explores these drugs, discussing their functions, usage, and the importance in maintaining cardiovascular health.
Read Now : Communication Strategies For Medication Adherence
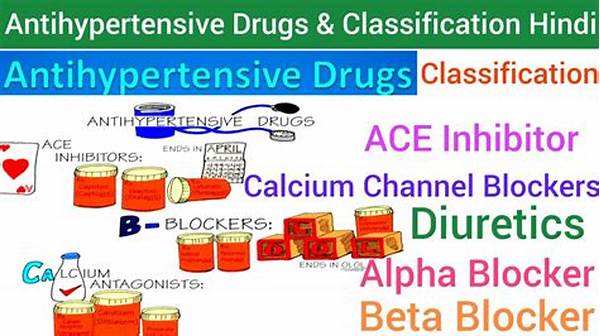
Common Classes of Antihypertensive Drugs
Popular antihypertensive drugs fall into several primary classes, each with distinct mechanisms of action that cater to varying patient needs. Beta-blockers, for instance, reduce the heart rate and the force of contraction, leading to a lowering of blood pressure. Calcium channel blockers work by relaxing and dilating the blood vessels, thereby easing blood flow. Diuretics, commonly referred to as water pills, help the kidneys eliminate excess sodium and water from the body, reducing blood volume and pressure. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) target hormonal systems in the body that regulate blood pressure, providing effective control. The diversity and specificity of these drug classes highlight the importance of personalized treatment plans, ensuring that patients receive the most suitable medication for their condition.
Benefits of Popular Antihypertensive Drugs
1. Effective Blood Pressure Control: Popular antihypertensive drugs are acclaimed for their capability to manage hypertension effectively, thereby reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
2. Diverse Mechanisms of Action: These drugs offer a range of mechanisms of action, allowing for versatile treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
3. Proven Track Record: With years of clinical use, popular antihypertensive drugs are well-documented in terms of efficacy and safety.
4. Improvement in Quality of Life: By managing blood pressure, these medications can significantly enhance a patient’s quality of life.
5. Reduced Risk of Secondary Conditions: Effective use of popular antihypertensive drugs decreases the likelihood of developing conditions such as heart attack and stroke.
The Role of Healthcare Providers in Medication Management
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in prescribing popular antihypertensive drugs and ensuring patients follow their treatment regimens accurately. Regular monitoring and follow-ups are essential to assess the effectiveness of the prescribed medication and to manage any possible side effects. It is their responsibility to educate patients about their condition, emphasizing the importance of adherence to prescriptions and lifestyle modifications for optimal outcomes. Patients are encouraged to engage in open communication with their healthcare providers, discussing any concerns or side effects they may experience. This collaborative approach fosters an environment of trust and informed decision-making, enhancing the overall effectiveness of hypertension management strategies.
Read Now : Enhancing Adherence Through Empathy Techniques
Patient Experiences with Popular Antihypertensive Drugs
For many patients, starting treatment with popular antihypertensive drugs marks a significant change in the management of their health. In everyday language, these meds are often termed “BP meds” or “blood pressure pills”. They’re known for being effective but can come with the occasional side effect like feeling dizzy or having a dry cough. However, many patients report a noticeable improvement in their energy levels and overall well-being once their blood pressure is under control. Keeping up with daily medication and routine check-ups becomes a part of life, but it’s all about keeping the heart healthy and ticking along smoothly. Sharing experiences with other patients helps, too, as it brings reassurance and tips on managing any hiccups along the way.
Mechanisms Underpinning Popular Antihypertensive Drugs
The efficacy of popular antihypertensive drugs is rooted in their biological mechanisms of action. Each class of medication operates differently within the cardiovascular system. For instance, beta-blockers inhibit the effects of adrenaline, leading to a slower heartbeat and reduced cardiac output, which subsequently lowers blood pressure. Conversely, ACE inhibitors prevent the formation of angiotensin II—a hormone that narrows blood vessels—thus facilitating vessel dilation and improved blood flow. Understanding these mechanisms allows healthcare practitioners to select the most appropriate drug based on the patient’s specific health profile and response to treatment, optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing potential adverse effects.
Trends and Developments in Antihypertensive Therapy
The landscape of antihypertensive therapy has evolved significantly, with a focus on enhancing drug efficacy and patient compliance. Advances in pharmacology have led to the development of combination medications, which incorporate two or more active ingredients to improve blood pressure control and simplify dosing regimens. This innovation aims to increase adherence by reducing the number of pills patients need to take daily. Additionally, ongoing research into the genetic and molecular basis of hypertension offers promising avenues for the discovery of novel therapeutic targets. As a result, the future of hypertension management may see increasingly personalized approaches, tailored to an individual’s genetic makeup and lifestyle, further advancing the field of cardiovascular medicine.
Closing Reflections on Popular Antihypertensive Drugs
In summary, popular antihypertensive drugs are indispensable in the management of high blood pressure and the prevention of related health complications. Their widespread use and proven track record underscore their importance in clinical practice. Nevertheless, the success of these medications extends beyond their pharmacological properties—it is equally dependent on the collaborative efforts of healthcare providers and patients. By fostering a deeper understanding of the medications and advocating for patient education and adherence, the full therapeutic potential of popular antihypertensive drugs can be realized. These efforts contribute not only to improved patient outcomes but also to the overall advancement of public health in addressing the global burden of hypertension.