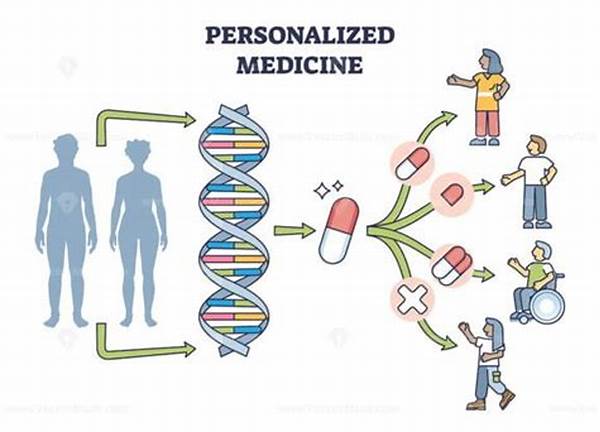
The Role of Genomic Research in Personalized Medicine
The advent of genomic research has marked a watershed moment in the field of personalized medicine, enabling the formulation of individualized treatment plans via genomic research. By decoding the intricate genetic blueprint of each patient, clinicians can now tailor therapies that are highly specific to the individual’s genetic makeup. This revolution in healthcare not only enhances the efficacy of treatments but also minimizes adverse effects, steering away from the one-size-fits-all model that has long dominated medical practices.
Read Now : Techniques For Inner Balance
Genomic research forms the foundation for understanding the complex interactions among genes, environment, and diseases. Leveraging this detailed understanding facilitates the development of individualized treatment plans that consider unique genetic mutations, predispositions, and responses to medications. As precision medicine continues to evolve, the integration of genomic data promises to optimize therapeutic strategies and prognostic assessments in a wide array of diseases, ranging from cancers to rare genetic disorders.
Although the application of genomic research in developing individualized treatment plans is still in its nascent stages, its potential is prodigious. As more genomic data is amassed and technology advances, personalized treatments will become increasingly accessible. This approach not only holds the promise of more effective healthcare but also heralds a paradigm shift in how diseases are perceived, diagnosed, and treated.
Benefits of Individualized Treatment Plans via Genomic Research
1. Precision in Therapy Selection: By focusing on an individual’s unique genetic composition, individualized treatment plans via genomic research enable clinicians to select the most effective therapies.
2. Enhancement of Drug Efficacy: By understanding genetic factors influencing drug metabolism, physicians can enhance the efficacy of medications through individualized treatment plans via genomic research.
3. Reduced Adverse Effects: Tailored treatment plans minimize the risk of adverse drug reactions, which are often due to genetic variability among individuals.
4. Identification of Risk Factors: Genomic analyses allow for the identification of genetic predispositions to certain diseases, aiding in early interventions.
5. Informed Prognostic Assessments: Personalized treatment plans contribute to more accurate prognostic assessments by accounting for genetic variability.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementing Genomic-Based Treatment Plans
The implementation of individualized treatment plans via genomic research is not without challenges. Chief among these is the ethical concern surrounding genetic data privacy. As genomic data becomes integral to healthcare, safeguarding patients’ genetic information from misuse and breaches is paramount. Implementing stringent data protection protocols and policies is essential to maintain trust and ensure the ethical application of genomic research in clinical settings.
Another significant hurdle is the integration of genomic research findings into everyday clinical practice. While the potential for individualized care is immense, translating complex genomic data into actionable treatment plans requires specialized knowledge and collaboration among geneticists, clinicians, and other healthcare professionals. Moreover, the cost of genomic testing and analyses remains a barrier for widespread adoption, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
Despite these challenges, the commitment to overcome these hurdles is strong, given the promising outcomes associated with individualized treatment plans via genomic research. As stakeholders continue to work collaboratively to address these issues, the widespread adoption of personalized medicine will gradually become a staple in healthcare.
Read Now : Genetic Profiling For Diseases
Genomic Advances Driving Individualized Treatment Discovery
Recent advances in genomic technology are the driving force behind the growing adoption of individualized treatment plans via genomic research. Comprehensive genomic sequencing techniques, such as whole-genome sequencing, provide comprehensive genetic insights that form the bedrock of personalized medicine. Such methodologies facilitate the identification of genetic mutations and variants, thereby informing the development of tailored therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, bioinformatics tools have significantly advanced the capacity to analyze and interpret the vast amounts of data generated through genomic research. These tools enable the synthesis of complex genetic data into clinically relevant insights, empowering healthcare providers to make informed decisions in designing individualized treatment plans. The collaboration of multidisciplinary teams in utilizing these technologies is crucial in translating raw genomic data into meaningful healthcare applications.
As the field continues to advance, the focus on combining genomic information with other omics data, such as proteomics and metabolomics, will further elevate the potential of individualized treatment plans via genomic research. This approach promises to deliver a holistic understanding of disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets, underscoring the transformative potential of genomics in healthcare.
Ethical Implications and Societal Challenges
In the realm of developing individualized treatment plans via genomic research, ethical considerations are paramount. Ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of genetic data must be of utmost significance. Developing robust frameworks and regulatory guidelines to address these ethical concerns is vital in fostering trust and promoting the responsible use of genomic information in medicine.
Moreover, equitable access to genomic-based treatments remains a societal challenge. The cost of genomic testing and tailored therapies may pose hindrances, especially within underserved communities. Thus, making these innovative healthcare solutions accessible and affordable is crucial in realizing the broader benefits of individualized treatment plans for all patients, irrespective of socioeconomic status.
Additionally, educating healthcare providers and patients about the potentials and limitations of genomic research is essential. Increasing genetic literacy will enable more informed dialogues between patients and clinicians, facilitating shared decision-making processes in the adoption of personalized treatment strategies. As the field evolves, continuous dialogue among stakeholders will be fundamental in navigating the complexities and fostering the ethical integration of genomic research into mainstream healthcare.
Future Prospects of Genomic Research in Medicine
Looking forward, the trajectory of individualized treatment plans via genomic research is anticipated to expand significantly. Integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies into genomic research holds promise for accelerating the discovery of novel genetic markers and therapeutic targets. Such integration will enhance the predictive modeling of patient responses to treatments and the evolution of diseases, ultimately catalyzing personalized medical breakthroughs.
Furthermore, ongoing research efforts focusing on diverse populations will enhance the generalizability and inclusivity of genomic databases. Recognizing and understanding genetic variations across different ethnicities will ensure that personalized treatment strategies are effective and applicable globally. The commitment to diversity and inclusion in genomic research is pivotal in addressing health disparities and ensuring that advancements benefit all of humanity.