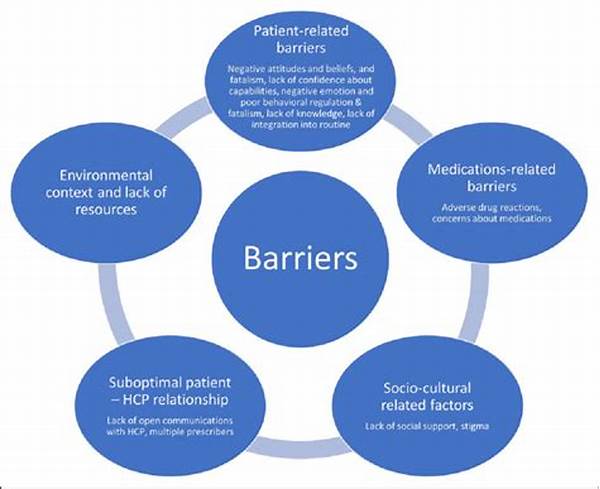
Medication adherence is a critical component of effective healthcare management, yet many patients face challenges in maintaining consistency with their prescribed regimens. Understanding the various barriers to medication adherence is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers striving to enhance patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs. This article delves into the multifaceted challenges that thwart patients’ efforts to adhere to prescribed therapies, and explores strategies to mitigate these barriers.
Read Now : Enhancer Regions In Different Tissues
Understanding Barriers to Medication Adherence
Barriers to medication adherence can be categorized into several key areas, including patient-related factors, healthcare system constraints, and medication-specific issues. Patient-related factors often encompass a lack of understanding about the condition or the importance of adherence, leading to suboptimal compliance. Additionally, psychological barriers such as depression or anxiety can impede a patient’s ability to adhere to their medication regimen. Moreover, cognitive impairments, common in elderly populations, can lead to forgetfulness in taking medications as prescribed.
Healthcare system constraints contribute significantly to barriers to medication adherence. In many cases, the complexity of obtaining medications—such as navigating insurance coverage, securing timely refills, or accessing pharmacies—can deter adherence. Furthermore, healthcare providers may inadvertently contribute to poor adherence through insufficient patient education or inadequate communication about the importance of sticking to prescribed treatments.
Medication-specific factors also present barriers to adherence. Complex regimens that require multiple doses throughout the day can be challenging for patients to manage. Moreover, side effects associated with certain medications can discourage patients from continuing their treatment. Additionally, the financial burden of medications, especially for those without adequate insurance coverage, remains a significant barrier.
Factors Influencing Barriers to Medication Adherence
1. Patient Understanding: A prevalent barrier to medication adherence is patients’ limited understanding of their condition and the importance of continuous treatment.
2. Psychological Barriers: Mental health issues such as depression and anxiety often interrupt consistent medication intake, highlighting a significant barrier to adherence.
3. Systemic Constraints: Navigating healthcare systems can create substantial barriers to medication adherence due to complex processes and accessibility issues.
4. Medication Complexity: Complex medication schedules can deter patients from maintaining a consistent regimen, leading to poor adherence.
5. Financial Challenges: The cost of prescriptions is a pressing barrier to medication adherence, particularly affecting those without comprehensive insurance coverage.
Addressing Barriers to Medication Adherence
Effective management of barriers to medication adherence involves a multifaceted approach. Educating patients about their health conditions and the significance of adherence is crucial. Empowering patients with knowledge enables them to make informed decisions and reinforces the necessity of maintaining their treatment regimens. Integrating reminders and support tools, such as mobile applications or pill organizers, can alleviate issues related to forgetfulness.
Healthcare systems also play a pivotal role in mitigating barriers to medication adherence. Streamlining processes to reduce the complexity of obtaining medications and increasing the accessibility of pharmacies can enhance adherence rates. Furthermore, healthcare providers should prioritize clear communication, ensuring that patients fully comprehend medication instructions and the potential consequences of non-adherence.
Addressing the economic barriers to medication adherence requires systemic changes. Efforts to lower prescription costs, expand insurance coverage, and provide financial assistance programs can significantly reduce the financial burden on patients. By addressing both individual and systemic challenges, the healthcare community can foster improved medication adherence and, consequently, better health outcomes.
Barriers to Medication Adherence Explained in Everyday Language
1. Forgetting Pills: Life’s busy, right? Sometimes people just forget to take their meds. This is a pretty common barrier to medication adherence.
2. Handling Side Effects: Nobody likes feeling worse from their meds! Side effects can definitely be a barrier to medication adherence.
3. Money Matters: If meds are too pricey, folks might skip them. That cost is a big barrier to medication adherence.
4. Complex Schedules: Taking multiple pills at different times can get confusing and is a barrier to medication adherence for many.
5. Health System Hurdles: Dealing with insurance and pharmacy waits? Those are serious barriers to medication adherence.
Read Now : “genomic Data-driven Medical Strategies”
6. Skipped Info: Not knowing why meds are important? That’s a barrier to medication adherence when info isn’t clear.
7. Mental Health Struggles: Anxiety and depression can make staying on track tough, creating barriers to medication adherence.
8. Trust Issues: Not trusting the doc or meds? A real barrier to medication adherence right there.
9. Transport Troubles: No way to get to the pharmacy is another barrier to medication adherence for people.
10. Language Barriers: If instructions aren’t in your language, that’s a huge barrier to medication adherence.
Overcoming Barriers to Medication Adherence
To effectively overcome barriers to medication adherence, healthcare organizations must adopt patient-centric strategies that incorporate a comprehensive understanding of individual patient needs. Collaboration between healthcare providers, patients, and caregivers is critical. Engaging in open dialogues helps to uncover specific challenges faced by patients, enabling the development of tailored interventions that cater to unique circumstances.
Educational programs focusing on patient empowerment are pivotal in overcoming barriers to medication adherence. Such programs should aim to improve health literacy and foster patients’ understanding of their medical conditions and the significance of consistent medication use. By equipping patients with the necessary knowledge and skills, they are better prepared to adhere to prescribed therapies, ultimately enhancing health outcomes.
Financial considerations also play a critical role in addressing barriers to medication adherence. Policymakers and healthcare providers must continually strive to alleviate the economic burdens faced by patients, potentially through initiatives such as reduced medication costs or expanded access to insurance coverage. Ensuring that patients can afford their medications is fundamental to fostering long-term adherence and sustaining health improvement.
Psychological Barriers to Medication Adherence
Psychological barriers can present significant challenges to medication adherence. Mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression often lead to diminished motivation or energy, which can result in missed doses and inconsistent adherence. Addressing these psychological barriers necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates mental health support into routine healthcare.
Healthcare providers can play a crucial role in recognizing and addressing psychological barriers to medication adherence. By conducting regular mental health assessments and fostering an environment of open communication, they can identify potential issues hindering adherence. Integrating mental health support services, such as counseling or therapy, with traditional medical treatment can help alleviate the psychological burdens that patients face, promoting better adherence.
Tailored intervention strategies that account for psychological barriers to medication adherence are vital. Collaborative care models that include mental health professionals can provide more holistic treatment plans, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of patient care. By prioritizing mental health in adherence efforts, healthcare providers can help patients achieve more consistent and successful treatment outcomes.
Summary of Barriers to Medication Adherence
In summary, barriers to medication adherence are multifactorial and encompass a range of challenges, including patient-related factors, healthcare system constraints, and medication-specific issues. These barriers often interconnect, creating complex scenarios that complicate efforts to improve adherence. Awareness and understanding of these barriers are crucial for healthcare providers aiming to enhance patient adherence and overall treatment effectiveness.
Addressing barriers to medication adherence requires a comprehensive, collaborative approach that focuses on patient education, healthcare system improvements, and economic interventions. Enhancing patient understanding through educational initiatives and clear communication can empower patients to take charge of their adherence. Meanwhile, systemic enhancements, such as improved access to medications and streamlined processes, can mitigate adherence challenges rooted in healthcare systems.
Financial solutions must also be prioritized to cushion the economic impact of medications on patients, thereby reducing cost-related adherence barriers. By addressing these multifaceted barriers with targeted strategies, healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients can make significant strides toward achieving better medication adherence and, ultimately, improve health outcomes for all.