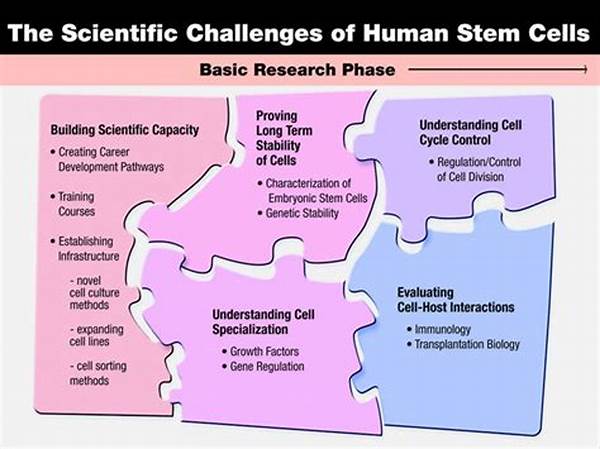
The quest for advancing stem cell research is akin to navigating a multifaceted landscape filled with promise and peril. The ability to scale stem cells holds potential to revolutionize regenerative medicine and personalized therapy, yet unforeseen challenges linger. Researchers are confronted with technical, economic, and ethical complexities that impede the progress necessary for clinical implementation.
Read Now : Epigenetic Regulation In Development
Technical Challenges in Stem Cell Scalability
The technical challenges in stem cell scalability remain some of the most formidable. To begin with, the consistent production of high-quality stem cells in large quantities is fraught with difficulties. Variations in cell potency and stability can arise due to disparities in environmental conditions during cultivation. Furthermore, the risk of genetic mutations increases as cells are multiplied, potentially hindering clinical applications. Additionally, specialized equipment and bioreactors needed for large-scale production necessitate significant investment and innovation. As researchers work to address these challenges in stem cell scalability, the need for standardized protocols and quality control mechanisms becomes increasingly evident.
Furthermore, overcoming these technical hurdles is essential for translating laboratory success into therapeutic realities. Scalable methods must ensure cell viability and functionality over extended periods. This includes maintaining the delicate balance of stem cell differentiation while preventing undesired cellular transformations. The pathway to scalability involves rigorous experimentation and cross-disciplinary collaboration to develop a unified framework that can be widely adopted.
Economic Considerations
1. Economic barriers stand as pivotal challenges in stem cell scalability, significantly affecting research and development.
2. High costs associated with raw materials and specialized tools pose significant challenges in stem cell scalability.
3. Complicated regulatory pathways impose additional challenges in stem cell scalability, increasing cost burdens on research entities.
4. Uneven funding and investment create financial viability challenges in stem cell scalability, limiting expansive research initiatives.
5. Collaborative efforts are essential to mitigate economic challenges in stem cell scalability, demanding innovation and resource allocation.
Ethical Challenges in Stem Cell Scalability
Ethical considerations present multifaceted challenges in stem cell scalability, raising moral dilemmas that require careful deliberation. The derivation and manipulation of stem cells, especially embryonic stem cells, evoke concerns regarding the sanctity of human life. These ethical debates necessitate a balance between scientific progress and societal values. Moreover, issues related to patient consent and data privacy stand as formidable barriers. Researchers and policymakers must navigate these ethical terrains to ensure that stem cell applications adhere to stringent ethical guidelines without stymying innovation.
Another dimension of the ethical challenges involves equitable access to therapies derived from stem cells. As scalability efforts advance, ensuring that these breakthroughs are accessible to diverse populations is paramount. This involves addressing disparities in healthcare systems, as well as potential exploitation concerns. A comprehensive ethical framework is critical to balancing innovation with responsibility, safeguarding the integrity of both scientific endeavors and societal principles. Thus, ongoing dialogue and ethical oversight remain crucial in overcoming challenges in stem cell scalability.
Exploring Challenges in Stem Cell Scalability
1. “Scaling up stem cells? Easier said than done!” Researchers are hitting major roadblocks trying to keep cell quality high while making gazillions of them.
2. “Dude, the tech for this is pricey!” The fancy gear and materials needed are making this a bank-breaker.
3. “Regulations? It’s like a maze!” Navigating through rules is adding layers to the struggle.
4. “Are we gonna leave some folks behind?” Accessibility and fairness are tough nuts to crack.
5. “Why’s it taking so long?” The path to success is full of trial and error.
Read Now : Genetic-based Personalized Treatment Strategies
6. “Science needs to get a move on!” Getting everyone on the same page for protocols is essential.
7. “Privacy is a big deal, man!” Keeping patient data safe is one of the real challenges.
8. “What’s fair play here?” Ethical issues are like a minefield.
9. “Who’s got the dough?” Funding is uneven, making expanding research challenging.
10. “Collab is key!” Joint efforts could make tackling these challenges smoother.
Overcoming Scientific Challenges
Addressing the scientific challenges in stem cell scalability necessitates a strategic approach focused on innovation and precision. Researchers are called to delve into advanced methodologies that can enhance the quality and quantity of stem cells produced. This involves exploring novel avenues in genetic engineering, bioinformatics, and materials science. The development of more sophisticated bioreactors and culture systems can lead to improved control over cellular environments, mitigating risks of contamination and genetic aberrations. By fostering interdisciplinary collaboration, scientists can expedite solutions to the technical challenges plaguing stem cell scalability.
In tandem, the pursuit of scalable technologies must align with robust quality control frameworks. The implementation of rigorous testing and validation processes is vital to ensure the reproducibility and consistency of stem cell production. Adopting standardized practices and protocols can streamline operations and foster global cooperation among research institutes. Moreover, addressing scalability challenges requires continuous investment in education and training programs to equip researchers with the necessary skills and knowledge. Ultimately, overcoming these obstacles can pave the way for groundbreaking applications in regenerative therapies and precision medicine.
Addressing Regulatory and Ethical Concerns
Navigating the regulatory and ethical challenges in stem cell scalability presents a complex yet crucial task for stakeholders. Regulatory frameworks must be agile enough to accommodate scientific advancements while ensuring safety and efficacy. Streamlining approval processes through adaptive compliance measures and proactive engagement with regulatory bodies can alleviate some of the bottlenecks faced by researchers. Harmonizing regulations across jurisdictions can promote international collaboration and facilitate the sharing of best practices.
Ethically, the equitable distribution of benefits derived from scalable stem cell solutions remains an imperative issue. Transparency in research methodologies and informed consent processes can enhance public trust and acceptance. Initiatives to increase diversity and inclusivity in clinical trials can address disparities and foster equitable access to stem cell therapies. Continuous dialogue among scientists, ethicists, and the public is essential to address evolving ethical challenges while affirming a commitment to responsible scientific conduct. By integrating ethical considerations with regulatory strategies, the path toward scalable stem cell innovations can be both ethically sound and scientifically robust.
Summary of Challenges
The journey toward achieving stem cell scalability is riddled with diverse challenges that demand a holistic and multifaceted approach. The quest to cultivate high-quality stem cells on a large scale is impeded by technical trials that necessitate cutting-edge technologies and interdisciplinary collaboration. Economic hurdles such as funding disparities and high production costs further complicate this endeavor, requiring strategic alliances and investments to sustain innovative research and development. Ethical dilemmas surrounding stem cell derivation and accessibility underscore the need for frameworks that balance scientific progress with moral imperatives.
Furthermore, the resolution of these challenges requires the integration of robust quality control measures and the alignment of international regulatory standards. Harmonizing these elements will facilitate the translation of laboratory successes into real-world applications. Continuous education and collaboration among scientists, policymakers, and stakeholders stand as cornerstones in overcoming the multifaceted challenges presented by stem cell scalability. Ultimately, addressing these barriers will unlock the transformative potential of stem cell therapies, heralding a new era in regenerative medicine and personalized health care.