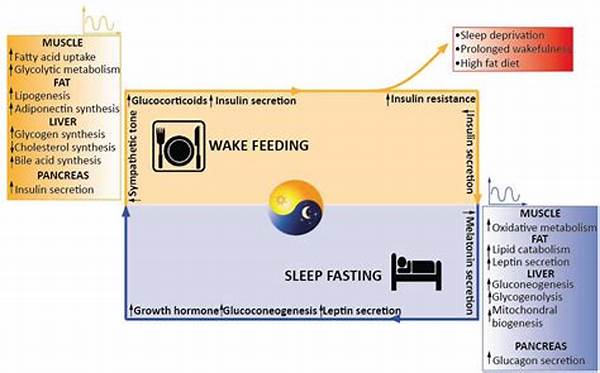
The field of circadian biology has garnered significant attention in recent years, particularly in its relation to drug metabolism. Circadian rhythms, the natural cycles of the biological processes within organisms, are responsible for regulating numerous physiological functions. This inherent biological timing system influences various aspects of pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, impacting how medications are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted. Understanding circadian biology in drug metabolism provides pivotal insights into optimizing pharmacotherapy and tailoring it to individual needs.
Read Now : Relationship Between Dosing Frequency And Efficacy
The Influence of Circadian Rhythms on Pharmacokinetics
Circadian biology plays a crucial role in drug metabolism by modulating the pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. The absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of pharmaceutical compounds are influenced by the body’s circadian rhythms. For example, liver enzymes responsible for metabolizing drugs exhibit diurnal variations, impacting their metabolic capacity at different times of the day. As a result, patients may experience varying drug efficacy and side effects depending on the timing of administration.
Moreover, circadian regulation also affects drug transporters and receptors involved in pharmacokinetics. This rhythmic modulation underscores the importance of considering dosing time when prescribing medications to maximize therapeutic outcomes and minimize adverse effects. The strategic alignment of drug administration with the body’s circadian rhythms is termed chronotherapy. By leveraging circadian biology in drug metabolism, healthcare professionals can optimize treatment efficacy and enhance precision medicine.
Key Aspects of Circadian Biology in Drug Metabolism
1. Liver Enzyme Activity: Circadian biology influences the activity of liver enzymes critical for drug metabolism, affecting drug clearance rates.
2. Chronotherapy: Timing medication administration according to circadian biology can enhance drug efficacy and reduce side effects.
3. Pharmacokinetics Variation: Circadian rhythms cause variations in drug absorption, distribution, and metabolism throughout the day.
4. Personalized Medicine: Understanding circadian biology allows for more personalized treatment approaches based on individual biological rhythms.
5. Therapeutic Windows: Circadian biology helps identify optimal therapeutic windows for drug administration, improving overall treatment outcomes.
Implications for Clinical Practice in Circadian Biology
Integrating circadian biology into clinical practice requires a paradigm shift in how healthcare is administered. The implications of circadian biology in drug metabolism are vast, necessitating adjustments in prescribing practices and patient education. Clinicians must consider the circadian timing of drug administration to enhance therapeutic efficacy while reducing adverse effects. This approach involves not only understanding the molecular underpinnings of circadian biology but also acknowledging its practical applications.
The growing body of research underscores the necessity for healthcare professionals to incorporate circadian biology principles into routine medical care. This includes educating patients about the significance of medication timing and fostering collaboration among interdisciplinary teams to devise strategies that optimize treatment regimens. By embracing circadian biology in drug metabolism, the medical community can ensure more effective and individualized patient care, ultimately advancing the field of precision medicine.
Read Now : Holistic Stress Control With Botanicals
The Future of Chronopharmacology
Chronopharmacology, the study of how biological rhythms influence drug effects, is an emerging field driven by advances in circadian biology. As our understanding deepens, there is immense potential for developing novel therapeutic strategies that leverage circadian rhythms. Innovations in this area may lead to the design of drugs with time-specific delivery mechanisms or formulations that align with the body’s natural cycles, enhancing drug efficacy.
Ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of circadian biology in drug metabolism. As the intricacies of circadian mechanisms are elucidated, there will be unprecedented opportunities for tailoring treatments to individual biological rhythms. The future of healthcare lies in harnessing these insights to refine drug development and delivery, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Considerations for Circadian Biology Research
Exploring the intricacies of circadian biology in drug metabolism requires meticulous attention to methodological design and data interpretation. Researchers must account for the multifaceted nature of circadian rhythms and their interaction with various biological systems. This entails adopting robust experimental frameworks that consider both intrinsic and extrinsic factors influencing circadian processes.
Interdisciplinary collaborations are essential to advancing the understanding of circadian biology in drug metabolism. Integrating insights from molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical sciences allows for comprehensive investigations into the temporal dynamics of drug action. Such endeavors enhance the translational potential of circadian biology research, facilitating its application in improving therapeutic strategies and patient care.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Circadian Principles
Implementing circadian biology in drug metabolism presents both challenges and opportunities within clinical settings. One key challenge is the variability in circadian patterns among individuals, which can complicate standardization of treatment protocols. However, this variability also presents an opportunity for personalized medicine, where treatment regimens are tailored to the unique circadian profiles of patients.
Furthermore, there is a need for increased awareness and education among healthcare professionals regarding the significance of circadian biology. By fostering a deeper understanding of how circadian rhythms influence drug metabolism, clinicians can make informed decisions that optimize treatment efficacy and reduce adverse effects. Embracing circadian principles holds the promise of revolutionizing medical practice, ushering in an era of precision medicine that aligns with the natural rhythms of the body.