The field of medicine has witnessed remarkable advancements over the past few decades, with one of the most promising being cell therapy. This cutting-edge therapeutic approach harnesses the potential of cells to treat various diseases, offering new avenues for improved patient outcomes. As research and technology in this area continue to evolve, the clinical applications of cell therapy have become a subject of significant interest among medical professionals and researchers alike.
Read Now : Ways To Increase Cognitive Endurance
Advances in Cell Therapy
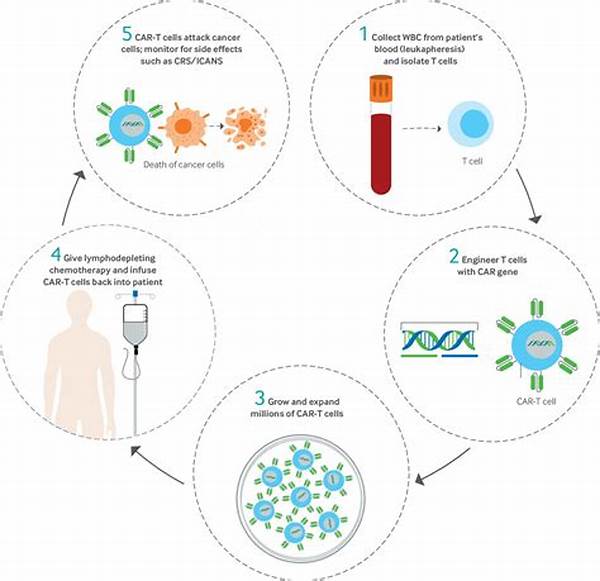
The clinical applications of cell therapy have seen significant progress, driven by advances in understanding cellular biology and regenerative medicine. One notable application is in oncology, where cell therapy is used to fight cancer. Techniques such as CAR T-cell therapy have shown promise in treating certain types of leukemia and lymphoma, providing new hope to patients who do not respond to traditional treatments. Additionally, cell therapy has found applications in treating chronic conditions like diabetes, where the use of stem cells offers a potential cure or significant improvement in disease management. The ability of cell therapy to tailor treatment to individual patient needs makes it a personalized approach to medicine, enhancing its effectiveness and minimizing side effects.
In the realm of neurology, the clinical applications of cell therapy are expanding rapidly. Neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s have long been challenging to treat effectively. However, recent studies have highlighted the potential of stem cells to replace damaged neurons and restore lost functions, offering a new frontier in neurological therapies. Similarly, cell therapy is being explored for its ability to facilitate tissue regeneration and repair in orthopedic conditions. For patients suffering from joint degeneration and injuries, cell-based treatments offer promising results in terms of pain reduction and improved mobility. The ongoing research in this field suggests a bright future for the integration of cell therapy into standard medical practice.
Another critical area where the clinical applications of cell therapy are making strides is in the treatment of autoimmune disorders. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis, which involve the body’s immune system attacking its tissues, have shown improvement with cell-based therapies. By modulating or replacing immune cells, these therapies aim to restore normal immune function and alleviate disease symptoms. As research in this field progresses, the potential to address a broader range of autoimmune diseases becomes increasingly feasible, highlighting cell therapy as a vital component of future therapeutic strategies. The ability of cell therapy to offer targeted and durable solutions underscores its revolutionary impact on modern medicine.
Challenges in Cell Therapy Implementation
1. The clinical applications of cell therapy are often hampered by regulatory challenges. Ensuring safety and efficacy requires rigorous testing and compliance with stringent guidelines, which can delay the availability of new treatments.
2. Scaling up production processes in the clinical applications of cell therapy remains a complex task. Producing sufficient quantities of high-quality cells that meet therapeutic needs is crucial for widespread adoption.
3. Cost remains a significant hurdle for the clinical applications of cell therapy. Developing and manufacturing cell-based treatments are resource-intensive, making them expensive for healthcare systems and patients.
4. Variability in patient response has been observed in the clinical applications of cell therapy. Individual differences in genetics and disease pathology can affect treatment outcomes, necessitating personalized approaches.
5. Ethical concerns related to the source of cells, particularly embryonic stem cells, pose challenges for the clinical applications of cell therapy. Addressing these concerns is essential for public acceptance and the advancement of therapies.
Future Prospects of Cell Therapy
The potential future pathways for the clinical applications of cell therapy are vast. With continued research and technological innovation, these therapies are poised to redefine the landscape of medical treatment. Collaborative efforts between scientists, clinicians, and industry stakeholders are essential to overcome current challenges and bring these therapies from the lab to the clinic. Personalized medicine, a key advantage of cell therapy, will likely play a pivotal role in the advancement of treatments, enabling therapies tailored to the unique genetic and biological characteristics of individual patients. Efforts to streamline manufacturing processes and reduce costs will be crucial in making cell therapy accessible to a broader patient population. As we look to the future, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in cell therapy research promises to accelerate the discovery of novel therapeutic targets and optimize treatment protocols.
Read Now : Anxiety-reducing Plant Extracts
Furthermore, public and private sector partnerships are expected to drive innovation in the clinical applications of cell therapy. Such collaborations can facilitate the sharing of knowledge, resources, and expertise, leading to accelerated progress in the field. Regulatory bodies worldwide are also working to establish clear guidelines and streamlined approval processes for cell therapy products, ensuring that safe and effective treatments reach the market promptly. The convergence of these efforts signifies a transformative era in medicine, where the clinical applications of cell therapy can offer durable and curative solutions to previously intractable diseases. The promising horizon of cell therapy underscores its potential to improve healthcare outcomes for millions worldwide.
Cell Therapy in Modern Medicine
The clinical applications of cell therapy in modern medicine represent a paradigm shift in how diseases are treated and managed. Unlike conventional therapies, which often concentrate on symptoms, cell therapy aims to address the root causes of diseases at a cellular level. This approach holds great promise in oncology, where therapies like CAR T-cell treatment are revolutionizing cancer care by reprogramming patient’s immune cells to specifically target and eliminate cancerous cells. Such innovations not only change the trajectory of cancer treatment but also offer hope to patients with otherwise limited options.
In regenerative medicine, the clinical applications of cell therapy are fostering new ways to repair and regenerate damaged tissues. This potential is evident in diseases that result in tissue degeneration, such as osteoarthritis, where cell-based interventions aim to regenerate cartilage and restore joint function. The impact of cell therapy in cardiology is also noteworthy, with ongoing studies exploring the use of stem cells to repair heart tissue following a heart attack. The integration of cell therapy with emerging technologies, such as 3D bioprinting, further amplifies its potential, paving the way for the creation of complex tissue structures that could someday lead to the development of lab-grown organs for transplantation.
Ethical Considerations in Cell Therapy Research
Ethical scrutiny is intrinsic to the clinical applications of cell therapy, given the complex terrain it navigates. The source of cells, particularly stem cells derived from embryos, continues to provoke ethical debates. Balancing scientific advancement with ethical responsibilities is paramount to ensure public trust and the harmonious progression of research. Furthermore, ensuring informed consent, particularly in experimental treatments, is critical in respecting patient autonomy and rights. Equitable access to these advanced therapies also poses ethical challenges, as high costs may limit patient access. By addressing these ethical dimensions, the clinical applications of cell therapy can be guided by principles of justice, beneficence, and transparency, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity and societal acceptance of medical innovations.
The ethical discourse surrounding the clinical applications of cell therapy extends to societal implications, such as potential genetic manipulation. Debates on gene editing, particularly germline editing, which could have enduring impacts on subsequent generations, require careful ethical consideration and robust policy-making frameworks. Public engagement in these discussions ensures diverse perspectives are considered, enabling the formulation of ethical guidelines that align with societal values. As cell therapy continues to evolve, maintaining a dialogue between scientists, ethicists, policymakers, and the public is essential to navigate the ethical challenges and foster a climate of trust and cooperation.
Summary: Transformative Impact of Cell Therapy
In summary, the transformative impact of cell therapy is increasingly evident across various medical domains, as it promises to revolutionize treatment paradigms by targeting diseases at their cellular roots. Its clinical applications span oncology, where cell therapy offers a new frontier in cancer treatment, providing targeted approaches like CAR T-cell therapy and other immune-based treatments. Cell therapy’s applicability extends to autoimmune diseases and chronic conditions such as diabetes, where it offers hope for disease modification or reversal by harnessing the regenerative capabilities of cells. This innovative approach underscores a shift towards personalized medicine, crafting treatments tailored to individual patient profiles, improving outcomes while minimizing side effects.
Furthermore, the realm of regenerative medicine benefits profoundly from the clinical applications of cell therapy. Through the use of stem cells and other cell types, medicine is on the cusp of breakthroughs in tissue regeneration, with significant implications for orthopedic and neurological conditions. The ability to regenerate damaged tissues and potentially restore lost functions signifies a monumental leap towards curative treatments. As ongoing research continues to unravel the complexities of cellular processes, the potential for cell therapy to address an even wider spectrum of medical challenges grows. The integration of new technologies and sustained collaborative efforts holds the promise of making cell therapy a cornerstone of future healthcare, offering enduring solutions to some of the most challenging medical conditions faced today.