Embryonic stem cell research represents a pivotal area of scientific inquiry that holds transformative potential for medical advancements. It involves the study of embryonic stem cells, which are pluripotent, meaning they have the capability to differentiate into any cell type in the human body. The therapeutic applications of this research are vast, offering hope for the treatment of numerous debilitating conditions. Recent developments in this field have sparked both excitement and ethical debates, making it a topic of significant scientific and public interest. This article delves into various aspects of embryonic stem cell research, presenting a comprehensive understanding of its scientific, ethical, and societal implications.
Read Now : Risk Evaluation For Medication Regimens
The Science Behind Embryonic Stem Cell Research
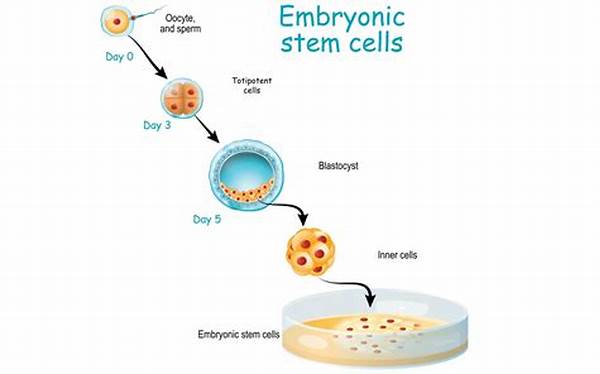
Embryonic stem cell research focuses on cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo. These stem cells are unique due to their remarkable ability to develop into virtually any type of cell in the human body, a property known as pluripotency. This characteristic makes them an invaluable resource for regenerative medicine, as they have the potential to replace damaged or diseased cells without the risk of immune rejection.
In recent years, advancements in embryonic stem cell research have accelerated, thanks to innovative techniques such as induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) technology. This method allows researchers to reprogram adult cells to a pluripotent state, mirroring the properties of embryonic stem cells, while bypassing some of the ethical concerns associated with using embryos. Despite these advancements, the original embryonic stem cells remain crucial for understanding the differentiation pathways necessary for developing effective treatments for diseases like Parkinson’s, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Ethical considerations often accompany discussions on embryonic stem cell research. The source of these cells—the destruction of embryos—raises significant moral questions. Balancing the potential benefits of research with respecting differing ethical perspectives is an ongoing challenge. As such, regulations and guidelines governing embryonic stem cell research vary worldwide, reflecting the diverse views on this complex issue.
Ethical Considerations in Embryonic Stem Cell Research
1. Ethical Dilemmas: The primary ethical dilemma in embryonic stem cell research lies in the destruction of human embryos, which some view as morally unacceptable despite potential medical benefits.
2. Legal Frameworks: Worldwide, countries have developed varying legal frameworks to address the ethical debates surrounding embryonic stem cell research, impacting the pace and nature of scientific progress.
3. Public Perception: Public opinion on embryonic stem cell research is shaped by cultural, religious, and ethical beliefs, which influence policy-making and funding availability.
4. Alternatives to Embryos: Advances in alternative technologies, such as iPSCs, aim to reduce reliance on embryonic stem cells, thus addressing ethical concerns while enabling continued scientific exploration.
5. Balancing Benefits and Ethics: Researchers strive to balance the potential breakthroughs offered by embryonic stem cell research with the need for ethical integrity and public trust.
Advances in Therapeutic Applications
The therapeutic applications emerging from embryonic stem cell research are potentially groundbreaking. With their ability to differentiate into any cell type, these cells present unique opportunities for regenerative medicine and the treatment of previously incurable conditions. Breakthroughs in this field could transform medical practices by providing new avenues for personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles and medical histories.
Moreover, embryonic stem cell research aids in drug discovery and development. By using these cells to model human diseases, scientists can better understand disease mechanisms and screen for potential therapeutic compounds. This accelerates the drug development process and enhances the precision of pharmaceutical interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing costs.
Despite its promise, the actual application of embryonic stem cell technology in clinical settings is still evolving, necessitating further research and rigorous clinical trials. The path from the laboratory to bedside is fraught with challenges, including ensuring the safety and efficacy of stem cell-derived treatments. Embryonic stem cell research remains a beacon of hope in modern medicine, with the potential to alleviate human suffering on an unprecedented scale.
Public Awareness and Engagement (Slang Style)
Yo, let’s chat about embryonic stem cell research! It’s a game-changer in the medical world, man. You’ve got these all-powerful cells that can turn into any type of cell in your body. Think about the possibilities! But yeah, there’s some drama with it too ‘cause it involves embryos. Check this out:
1. Stem Cells Rock: They’re like the superheroes of cells, ready to fight disease and take on anything.
2. Ethics Debate: Not everyone’s on board, bro. Some folks get iffy about where these cells come from.
3. Breakthroughs, Baby: We’re talking potential cures for stuff that’s been untouchable till now.
4. Law Dance: Different places have their rules, so the research isn’t cruising at the same pace everywhere.
5. Switching It Up: Scientists are finding new ways to get similar cells without the ethical baggage. Cool, right?
6. Why Care?: It’s not just for science geeks. This could impact us all with new medical treatments.
Read Now : Side Effects Of Mixing Multiple Medicines
7. Funding Hustle: Money makes the world go round, and research like this needs serious cash flow.
8. Tech Talk: The gear and methods in this space are bonkers. Cutting-edge stuff, for sure.
9. Future Forward: The future’s looking bright with this tech, but it needs right handling, ya know?
10. Big Picture: It’s about more than science. It’s a mix of beliefs, laws, and super tech.
Challenges in Implementation of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Embryonic stem cell research, while promising, encounters several significant challenges that impede its swift translation from laboratory research to clinical application. These challenges are multifaceted, involving technical, ethical, and regulatory hurdles that must be addressed to fully realize the potential of this revolutionary field.
Firstly, the technical complexity of manipulating embryonic stem cells into specific cell types is a primary challenge. Although these cells are pluripotent, directing their differentiation reliably and safely into the desired cell types remains a formidable task. Researchers continue to work on refining differentiation protocols and ensuring the stability of these cells once transplanted.
In addition to technical challenges, ethical issues pose substantial obstacles. The use of human embryos in research raises moral questions, leading to public debates and varying degrees of legal restrictions across different countries. These regulatory differences create an uneven landscape for research advancement, affecting international collaboration and slow down progress.
Furthermore, the safety of stem cell-based therapies is critically important. Addressing safety concerns requires extensive clinical trials to ensure that treatments do not lead to unintended consequences, such as the formation of tumors. Hence, stringent oversight and robust clinical research are fundamental to advancing embryonic stem cell applications safely.
Future Directions in Embryonic Stem Cell Research
The future of embryonic stem cell research is poised for remarkable advancements, driven by the convergence of scientific innovation and evolving ethical considerations. Researchers are increasingly exploring novel methodologies to overcome current limitations and enhance the therapeutic potential of stem cells.
Emerging technologies, such as CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing, offer possibilities to further refine stem cell applications by facilitating precise genetic modifications. This could lead to personalized medicine approaches, where treatments are tailored to individual genetic profiles, significantly enhancing efficacy and patient outcomes.
Moreover, the focus is shifting towards alternative sources of pluripotent cells, such as induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which circumvent ethical concerns associated with embryonic sources. This shift not only bolsters public support but also accelerates research by broadening the scope of possible cell lines available for study.
As the field progresses, interdisciplinary collaborations between biologists, ethicists, and policymakers are crucial. These partnerships can guide responsible research and application, ensuring that scientific progress aligns with societal values and ethical norms, ultimately paving the way for breakthroughs that transform healthcare.
Summary of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Embryonic stem cell research continues to be a cornerstone of scientific exploration, offering unprecedented opportunities for understanding human development and disease treatment. Its hallmark feature, pluripotency, grants researchers the ability to investigate an array of cellular processes and develop new therapeutic strategies. This research is instrumental in the quest to address complex medical conditions like neurodegenerative diseases, where traditional methods have fallen short.
Despite its potential, embryonic stem cell research is fraught with ethical considerations, particularly concerning the source of these cells. This ethical dimension necessitates ongoing dialogue and careful regulatory oversight to ensure that research advances align with public values and ethical standards. Consequently, the field is subject to a broad spectrum of regulations worldwide, reflecting diverse sociocultural perspectives.
Looking forward, the integration of cutting-edge technologies and alternative cell sourcing methods holds promise for overcoming current hurdles. As researchers continue to refine techniques and explore new possibilities, embryonic stem cell research remains central to the future of personalized and regenerative medicine, offering hope for transformative health interventions. The collaborative efforts of scientists, ethical bodies, and policymakers will be paramount in steering this promising field toward its full potential, ensuring that its benefits are realized responsibly and equitably.