The integration of genomic data into medical care represents a revolutionary shift in the way healthcare is delivered and personalized. By leveraging the vast information contained within the human genome, medical professionals are now able to tailor treatments and preventive measures that align more precisely with individual genetic profiles. This movement towards precision medicine is transforming patient outcomes and continues to shape the future landscape of healthcare.
Read Now : Mindfulness Practices For Reducing Stress
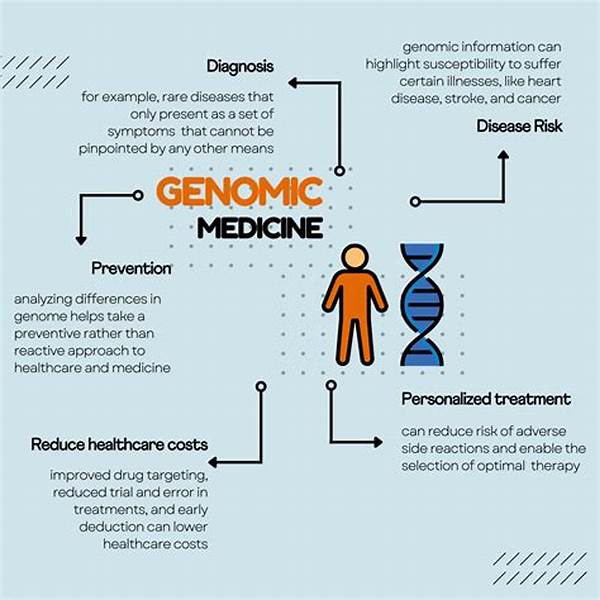
The Importance of Genomic Data in Personalizing Medicine
Genomic data in medical care plays a pivotal role in personalizing medicine. This innovative approach is enabled by technological advancements that allow for comprehensive analysis of genetic information. Such data helps in identifying genetic predispositions to certain conditions, which in turn guides healthcare providers in crafting proactive interventions and customized therapies. For instance, genomic data can reveal a patient’s likelihood of developing diseases such as cancer, enabling early interventions that significantly improve prognoses. Furthermore, genomic insights enhance drug efficacy and safety by determining how individuals metabolize medications, thus reducing adverse drug reactions. In essence, the utilization of genomic data in medical care optimizes healthcare delivery, fostering a proactive rather than reactive approach to health management. It empowers patients with knowledge about their genetic make-up, enabling informed decisions and promoting a participatory role in managing their health. As such, the personalization of medical care through genomic data not only holds promise for enhancing the quality of life but also in reducing the overall burden on healthcare systems globally.
Challenges in Implementing Genomic Data
1. Implementing genomic data in medical care requires overcoming significant logistical challenges, including data storage and management.
2. Ethical considerations arise, as genomic data utilization must protect patient privacy and confidentiality in medical care.
3. Integration into existing healthcare systems is complex, demanding technological advancements and professional training.
4. Costs associated with genomic data analysis remain a barrier to widespread accessibility in medical care.
5. Standardization of practices and data interpretation is essential for consistent application of genomic data in medical care.
The Future of Genomic Data in Disease Prevention
The future of genomic data in disease prevention holds unprecedented potential. As research progresses, the ability to predict and mitigate health conditions before they manifest could become a standard aspect of medical care. Genomic data enables healthcare professionals to map an individual’s genetic risk factors with precision, tailoring preventive strategies accordingly. This anticipatory approach not only enhances patient outcomes but also contributes to the sustainability of healthcare systems by prioritizing preventive over curative measures. In addition, as collaborations between geneticists, clinicians, and technologists continue to evolve, the scalability and accessibility of genomic data tools are likely to improve. These advancements could democratize the benefits of genomic insights, making personalized preventive care a universal standard rather than a privilege. As a result, genomic data in medical care is set to not only transform individual health management but also redefine preventive paradigms across populations.
Genomic Data in Everyday Medical Practice
1. Genomic data in medical care is becoming a staple, influencing decisions from routine check-ups to complex surgeries.
2. Doctors use genomic insights to prescribe medications with higher success rates and fewer side effects.
Read Now : Stress-reducing Herbal Tea Guide
3. Patients receive personalized lifestyle recommendations based on their unique genetic profiles.
4. Early detection of genetic conditions through genomic data is saving lives and reducing healthcare costs.
5. Genomic data informs reproductive planning, aiding prospective parents in understanding genetic risks.
Ethical Implications of Genomic Data Utilization
The integration of genomic data in medical care has ushered in a new era of personalized medicine, yet it also raises significant ethical concerns. Patient privacy and consent are paramount, as genomic data contains deeply personal and sensitive information. Ensuring that individuals fully understand the implications of sharing their genetic information is a critical ethical consideration in medical practice. Furthermore, the potential for genetic discrimination by insurers, employers, or other entities necessitates robust legal protections. Equitable access to genomic technologies is another ethical aspect, as disparities in access could lead to inequalities in healthcare outcomes. Policymakers and healthcare providers must work collaboratively to address these ethical challenges, ensuring that the benefits of genomic data in medical care are realized without compromising individual rights.
Training Healthcare Professionals
The successful integration of genomic data in medical care hinges on the proper training of healthcare professionals. As genomic technologies continue to evolve, medical practitioners must possess the requisite knowledge and skills to effectively interpret and apply genomic data in clinical settings. This necessitates curriculum enhancements in medical education and ongoing professional development opportunities. By ensuring that healthcare providers are equipped with genomic literacy, the potential of genomic data to transform patient care can be fully realized. Moreover, interdisciplinary collaboration, involving geneticists, bioinformaticians, and clinicians, will be essential in harnessing the full potential of genomic insights. The commitment to training and education ensures that healthcare professionals remain at the forefront of this rapidly advancing field.
Summary of Genomic Data in Medical Care
Genomic data in medical care represents a paradigm shift towards highly personalized healthcare solutions, marking a significant departure from traditional, one-size-fits-all approaches. By analyzing a person’s genetic blueprint, healthcare providers can predict susceptibility to diseases, optimize treatment plans, and even anticipate potential adverse drug reactions. This data-driven approach not only enhances the effectiveness of medical interventions but also aids in the prevention of diseases, transforming patient outcomes and fostering a proactive rather than reactive healthcare model. The integration of genomic data into daily medical practice holds transformative potential. However, it also poses ethical and logistical challenges that must be addressed. Ensuring data privacy, obtaining informed consent, and safeguarding against genetic discrimination are crucial to maintaining patient trust and ensuring equitable access to genomic technologies. Additionally, training healthcare professionals to interpret and utilize genomic data is paramount for the successful application of these insights in clinical settings. As the field continues to evolve, collaborative efforts among geneticists, clinicians, policymakers, and technology developers will be key to overcoming these challenges and unlocking the full potential of genomic data in medical care, ultimately setting a new standard for personalized and preventive healthcare.