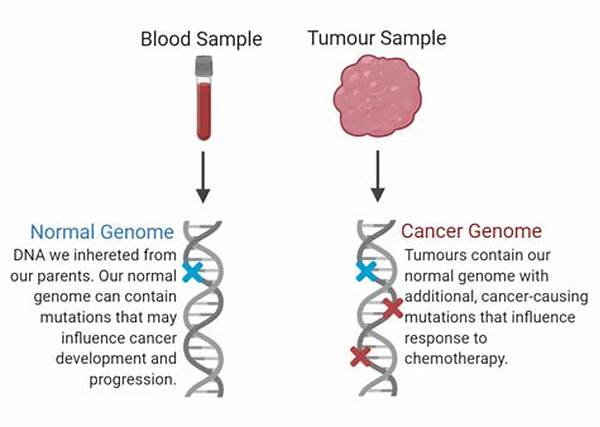
The Role of Genomics in Personalized Treatment
In the realm of oncology, advancements in genomics have transformed the landscape of cancer treatment, offering promising avenues for individualized therapy. Genomics in individualized cancer therapy refers to the utilization of genomic information—pertaining to the genetic makeup of an individual and their tumor—to guide personalized treatment strategies. This approach is based on the understanding that each patient’s cancer is unique, driven by specific genetic mutations that influence tumor behavior and response to therapy.
Read Now : **robotic-assisted Surgical Systems**
The integration of genomics in individualized cancer therapy allows for the identification of actionable mutations and biomarkers that can serve as potential targets for treatment. By analyzing the genomic profile of a patient’s tumor, oncologists can select therapeutics that specifically target the genetic alterations present, thereby increasing the likelihood of treatment efficacy. Furthermore, this method enables the identification of patients who may benefit from targeted therapies or immunotherapies, thereby reducing the exposure to ineffective treatments and minimizing adverse effects.
Overall, genomics in individualized cancer therapy represents a paradigm shift from the traditional one-size-fits-all approach to a more tailored strategy that considers the genetic uniqueness of each patient. It underscores the potential for genomics to not only enhance treatment outcomes but also contribute to the advancement of precision medicine in oncology. The integration of such innovative approaches in clinical practice continues to evolve, offering hope and promise for improved patient care and outcomes.
Key Aspects of Genomics in Individualized Cancer Therapy
1. Targeted Drug Delivery: Genomics in individualized cancer therapy enables the precise targeting of tumor-specific genetic mutations, leading to improved treatment outcomes and reduced systemic toxicity.
2. Biomarker Identification: Through genomics, specific biomarkers associated with cancer progression can be identified, facilitating better risk stratification and treatment planning.
3. Resistant Mechanisms Insight: Understanding the genomic alterations helps in deciphering mechanisms of resistance to therapy, offering opportunities to develop strategies to overcome such hurdles.
4. Customized Treatment Plans: Individualized genomic data allow for the customization of therapy regimens based on the specific genetic profile of the patient’s cancer, enhancing the precision of treatment.
5. Prognostic Indicators: Genomics in individualized cancer therapy provides valuable prognostic markers that can predict patient outcomes and guide the clinical decision-making process.
Challenges and Opportunities in Genomics-Driven Therapy
The incorporation of genomics in individualized cancer therapy presents both significant opportunities and challenges. One of the primary opportunities lies in the ability to develop therapies that are highly specific to an individual’s cancer, thereby increasing the likelihood of treatment success while minimizing adverse effects. Genomic profiling allows for the accurate identification of therapeutic targets, which is crucial in the design of personalized treatment regimens.
However, challenges persist, including the complexity of cancer genomics, which involves numerous mutations that may vary not only between patients but also among different tumor sites within the same individual. Moreover, the interpretation of genomic data requires sophisticated bioinformatics tools and expertise, posing a barrier to its widespread adoption in clinical settings. Additionally, ethical and logistical considerations, such as the cost of genomic testing and data privacy concerns, require careful attention to ensure equitable access to such advanced therapies.
Despite these challenges, the future of genomics in individualized cancer therapy is promising, with continued research and technological advances expected to address existing obstacles. As our understanding of the genomic underpinnings of cancer deepens, it is anticipated that personalized cancer therapy will become an increasingly integral component of comprehensive cancer care, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
The Evolution of Genomics in Cancer Treatment
As the field of oncology advances, the integration of genomics in individualized cancer therapy has emerged as a cornerstone of modern cancer care. The transition from conventional treatment modalities to personalized strategies has been driven by a greater understanding of cancer biology and genomic technologies. This shift signifies a move toward therapies that are not only more effective but also tailored to the individual genetic profiles of patients and their tumors.
Read Now : Safe Medication Storage Practices
Genomics in individualized cancer therapy involves the utilization of high-throughput sequencing technologies to interrogate the entire genomic landscape of cancer cells. By identifying mutations, alterations, and epigenetic modifications, this approach allows for a more comprehensive view of the molecular drivers of cancer. The insights gained from genomic data are instrumental in identifying new therapeutic targets and developing innovative treatment modalities that cater to the heterogeneous nature of cancer.
As new discoveries continue to emerge, the role of genomics in cancer therapy is expected to expand, paving the way for the integration of multi-omics approaches that incorporate proteomic, transcriptomic, and metabolomic data. These advancements promise to enhance our ability to diagnose cancer earlier, offer more effective treatment options, and ultimately transform the way we approach cancer management. The integration of genomics in individualized cancer therapy therefore heralds a new era of precision medicine that holds the potential to revolutionize cancer treatment paradigms.
Clinical Implementation and Future Perspectives
The clinical implementation of genomics in individualized cancer therapy is an ongoing and evolving process. The translation of genomic discoveries into clinical practice requires robust infrastructure and collaboration among multidisciplinary teams, including clinicians, geneticists, and bioinformaticians. The establishment of standardized guidelines and protocols for genomic testing and interpretation is critical to ensure the validity and reliability of results that guide treatment decisions.
Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials and research initiatives are pivotal in assessing the efficacy of genomics-driven treatment strategies and identifying novel biomarkers for different cancer types. As our knowledge expands, it is anticipated that genomics in individualized cancer therapy will become increasingly integrated with routine cancer care, supported by policy frameworks that facilitate access and reimbursement for genomic testing.
Looking to the future, advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning are expected to further enhance the predictive power of genomic data, offering deeper insights into cancer biology and therapeutic responses. The potential to combine genomic information with real-world data also presents opportunities to refine treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes. Ultimately, the promise of genomics in individualized cancer therapy lies in its ability to provide targeted interventions that address the specific genetic underpinnings of a patient’s cancer, ushering in a new era of precision oncology.
Summary and Conclusion
In conclusion, the incorporation of genomics in individualized cancer therapy marks a transformative advancement in the field of oncology. The ability to harness genomic information to tailor treatment strategies represents a significant departure from traditional approaches and holds remarkable promise for improving patient outcomes. By targeting the specific genetic alterations driving a patient’s cancer, genomics-driven therapies offer the potential for enhanced efficacy and reduced side effects.
The implementation of genomics in individualized cancer therapy faces challenges, including the need for comprehensive understanding and interpretation of complex genomic data, as well as addressing ethical, logistical, and financial considerations. However, as research progresses and technologies advance, it is anticipated that these challenges will be overcome, facilitating broader access to personalized treatment options.
Ultimately, genomics in individualized cancer therapy underscores the dynamic evolution of cancer treatment and the shift toward precision medicine. As our understanding of cancer biology continues to grow, the integration of genomics into clinical practice promises to revolutionize the management of cancer, leading to more effective and personalized therapeutic interventions. The ongoing commitment to research and innovation in this field remains essential to fully realize the potential of genomics in transforming the landscape of cancer care.