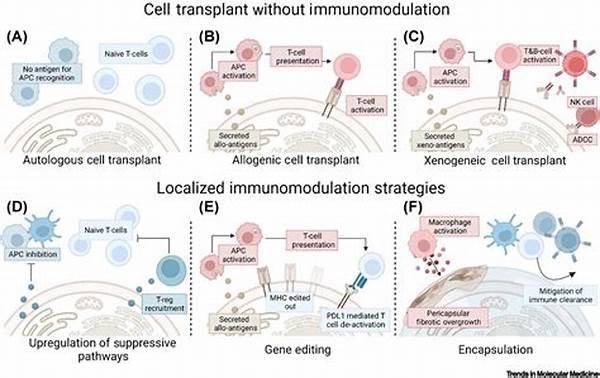
In recent years, the field of medicine has witnessed a transformative shift towards personalized treatments and regenerative medicine. At the heart of these advancements lies immunomodulation in cell therapy, a process that seeks to harness and manipulate the body’s immune system to treat a variety of diseases. This innovative approach offers promising avenues for effectively managing and potentially curing chronic and acute conditions that were previously deemed challenging to treat.
Read Now : Stress Management Herbal Tea Choices
The Role of Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy
The concept of immunomodulation in cell therapy revolves around the ability to modulate the immune response through therapeutic interventions. These interventions can either amplify the immune system to fight against specific ailments or suppress it to prevent autoimmune reactions. In essence, immunomodulation in cell therapy tailors immune responses to meet the specific needs of individual patients, vastly enhancing therapeutic outcomes. Recent developments in biotech have facilitated the manipulation of immune cells, rendering them more potent and targeted in their action. This not only reduces side effects but also improves the efficacy of treatments. Furthermore, this approach offers significant implications for diseases such as cancers, autoimmune disorders, and infectious diseases. By understanding and controlling the pathways of immune response, researchers and clinicians can develop treatments that are both precise and personalized. The potential applications of immunomodulation in cell therapy represent a paradigm shift in how we approach treatment across various medical fields.
Mechanisms of Action in Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy
1. Immunomodulation in cell therapy utilizes T-cells to recognize and eliminate cancer cells, providing a targeted and effective treatment option.
2. Regulatory T-cells play a pivotal role in immunomodulation by maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing unwanted inflammation.
3. Dendritic cells are employed in immunomodulation in cell therapy to enhance antigen presentation, thereby strengthening the immune response.
4. Mesenchymal stem cells can act as immunomodulators, exerting anti-inflammatory effects to treat autoimmune conditions.
5. The integration of immunomodulation in cell therapy with CRISPR technology offers precision editing of the immune system for enhanced treatment efficacy.
Clinical Applications of Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy
The integration of immunomodulation in cell therapy into clinical practice is already underway, with several trials showcasing promising results. Immunomodulation in cell therapy is particularly efficacious in oncology, where immune cells are engineered to specifically target and destroy malignant cells, offering a precision strategy that minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissues. Furthermore, beyond oncology, there is a growing interest in employing this approach to tackle autoimmune diseases where the immune system erroneously attacks the body’s own cells. By selectively suppressing hyperactive immune responses, researchers aim to offer relief to those suffering from conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. The therapeutic landscapes for chronic infections, organ transplants, and inflammatory diseases are also expanding with the introduction of immunomodulation strategies in cell therapy, allowing for broader treatment possibilities. As ongoing research continues to reveal new insights into cellular pathways and immune interactions, the scope and success rates of immunomodulation in cell therapy are expected to grow exponentially, heralding a new era of medicine.
Read Now : Concepts Of Chi Flow
Challenges and Future Perspectives in Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy
Though immunomodulation in cell therapy holds considerable promise, challenges remain in its delivery and efficacy at a broader scale. The complexity of human immune responses requires an intricate understanding of cell behavior and signaling pathways. Researchers must overcome challenges related to the longevity of modified cells, managing potential off-target effects, and ensuring the scalability of manufacturing processes. Collaboration among multidisciplinary teams is essential to surmount these hurdles, necessitating concerted efforts across research institutions, biotech companies, and regulatory bodies. Looking forward, the future of immunomodulation in cell therapy hinges on continued investment in fundamental research and the translation of laboratory findings into clinical practice. By pushing the boundaries of what is possible, scientists and clinicians are paving the way for a new era where treatments are not only innovative but also safe, targeted, and highly effective.
Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy: Therapeutic Innovations
Immunomodulation in cell therapy represents a burgeoning field with striking therapeutic innovations that are revolutionizing treatment modalities. By focusing on the nuanced interactions within the immune system, researchers have been able to develop therapies with unprecedented specificity and effectiveness. This is particularly evident in the realm of CAR-T cell therapies, where patient-specific T-cells are engineered to target tumor-specific antigens, providing a groundbreaking approach to cancer treatment. Additionally, the use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) offers a promising avenue for generating patient-specific immune cells, thus circumventing issues of immunogenicity and ensuring more personalized treatment protocols. As these therapeutic innovations continue to evolve, the landscape of modern medicine is poised to change dramatically. The application of immunomodulation in cell therapy extends beyond immediate clinical benefits, offering hope in understanding and combating complex diseases. These advancements not only highlight the potential of precision medicine but also set the stage for future breakthroughs.
Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy: Patient-Centric Approaches
The implementation of immunomodulation in cell therapy signifies a shift towards more patient-centric approaches in medical treatments. By focusing on the individual’s unique genetic and immunological profile, treatments can be tailored to maximize efficacy and minimize adverse effects. This personalization is integral to enhancing patient outcomes and has been exemplified in the treatment of hematologic malignancies where tailored cell therapies have shown remarkable success. Furthermore, patient-centric approaches necessitate the involvement of patients in decision-making processes, empowering them to actively participate in their health care journeys. The principles underpinning immunomodulation in cell therapy demand a paradigm shift in how medical professionals engage with patients, embracing a holistic view that incorporates both scientific advancements and patient preferences. This shift towards personalized medicine through immunomodulation in cell therapy underscores the importance of integrating cutting-edge science with compassionate care, ultimately fostering a deeper connection between advances in medical technology and patient well-being.
Conclusion: The Promise of Immunomodulation in Cell Therapy
In conclusion, immunomodulation in cell therapy offers a promising horizon for the future of medicine, transforming the way we approach and treat complex diseases. By precisely altering immune responses, this approach provides a dynamic tool for clinicians to either enhance or suppress immune activity as needed, offering customizable solutions to a range of health challenges. As we continue to expand our understanding of the intricate immune landscape, the potential for even more refined and effective treatments becomes increasingly attainable. The commitment to advancing immunomodulation in cell therapy reflects a broader dedication within the medical community to innovation, patient-centered care, and the pursuit of healing through modern scientific exploration. It emphasizes the importance of collaborative efforts in pushing the boundaries of what is possible, providing hope and solutions for previously untreatable conditions. As we stand on the cusp of these advancements, the integration of immunomodulation into therapeutic strategies is poised to redefine the standard of care and set new benchmarks in medical treatment efficacy and safety.