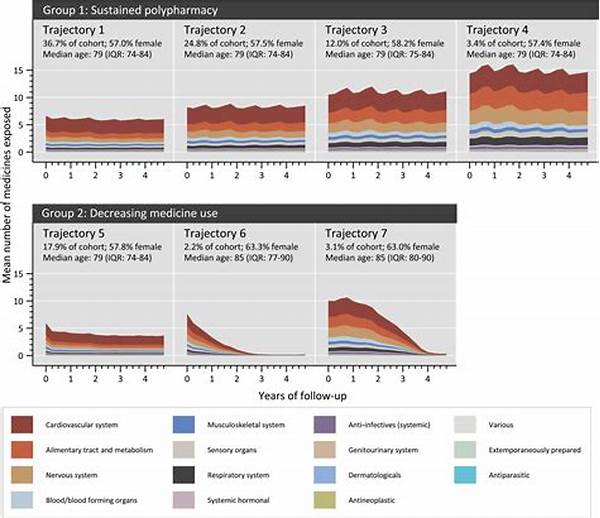
Polypharmacy, defined as the concurrent use of multiple medications by a patient, is a growing concern in the healthcare sector, particularly among adults. With the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases and the expanding pharmaceutical market, patients often find themselves on complex medication regimens. While polypharmacy can be essential for managing multiple health conditions, it is imperative to understand that the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults can lead to significant health challenges. This article explores these effects, offering a comprehensive overview of the implications of long-term medication use and highlighting the importance of careful medication management.
Read Now : Dna Sequencing For Patient-specific Medicine
Health Implications of Long-term Polypharmacy
The long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults include both physiological and psychological consequences. Physiologically, prolonged use of multiple medications can lead to drug interactions, which may cause adverse reactions or reduce the efficacy of the drugs. This interaction is particularly dangerous in the elderly, who often have slower drug metabolism, increasing their susceptibility to drug toxicity. Furthermore, the kidneys and liver, which are critical in drug clearance, may be overburdened, leading to potential organ damage or failure.
Psychologically, the burden of managing multiple medications can lead to confusion, anxiety, and cognitive decline. Patients may become overwhelmed by the complexity of their treatment regimens, resulting in decreased adherence to medication schedules. This non-adherence not only diminishes the therapeutic effectiveness but may also exacerbate existing medical conditions, requiring additional medications and further complicating patient care.
Additionally, the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults have socio-economic implications. The financial burden of purchasing numerous medications can be substantial, leading to increased healthcare costs for individuals and systems. This financial strain can discourage individuals from maintaining their medication regimens, ultimately compromising their health. Thus, it is vital for healthcare providers to regularly review and optimize patients’ medication regimes to minimize unnecessary or harmful prescriptions.
Causes and Contributing Factors of Polypharmacy
1. The long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults often stem from inappropriate prescribing practices, where medications are prescribed without a thorough review of the patient’s current regimen.
2. Chronic health conditions frequently necessitate complex treatments, yet they also contribute to the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults as patients often receive multiple prescriptions.
3. Limited communication between healthcare providers can lead to fragmented care and the unintentional long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults as no single provider has a complete view of the patient’s medication list.
4. Patients’ self-medication and the use of over-the-counter drugs add to the complexity of their regimen, amplifying the risk of the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults.
5. The aging population is particularly vulnerable to the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults due to the prevalence of multi-morbidity requiring numerous medications.
Strategies for Managing Polypharmacy
To mitigate the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults, healthcare providers must adopt systematic approaches. Comprehensive medication reviews conducted at regular intervals are crucial for assessing and adjusting treatment plans. This involves evaluating the necessity, efficacy, and safety of each medication within the context of the patient’s current health status. Regular reviews can prevent the unnecessary continuation of medications and minimize the risk of adverse drug interactions.
Moreover, patient education plays a pivotal role in managing the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Educating patients about their medications, including their purposes and potential side effects, can empower them to become active participants in their healthcare. This knowledge serves to enhance medication adherence and encourages individuals to report any adverse effects experienced, facilitating timely interventions by healthcare providers.
Interprofessional collaboration is another crucial element in managing the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. By fostering open communication and coordination among pharmacists, nurses, and physicians, healthcare teams can ensure comprehensive and cohesive care plans. This teamwork allows for adjustments to be made promptly and effectively, ensuring optimal patient outcomes and reducing the risk of adverse events associated with polypharmacy.
Common Misconceptions about Polypharmacy
Long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults can often be misunderstood. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Many think it’s unavoidable as we age, but that’s not true. Regular med reviews can help!
2. People assume more drugs mean better results. Not always—the interactions can get tricky.
Read Now : Scheduling Medication Intake For Optimal Results
3. “I feel fine, so it must be working.” Symptoms might be quiet, but it’s not foolproof.
4. Stopping meds suddenly is okay. Nope, that can be super risky!
5. Only old folks deal with this. While seniors are prone, younger adults can face it too.
Factors Influencing Polypharmacy
A multitude of factors contribute to the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Demographic variables, such as age and gender, play significant roles, with older adults and women more frequently experiencing polypharmacy. This demographic predisposition is often due to the higher prevalence of chronic diseases within these populations, necessitating multiple treatments. Additionally, patients receiving care from multiple healthcare providers without integrated communication systems are at greater risk. This lack of coordination can lead to duplicated prescriptions or the continuation of outdated medication regimens, exacerbating the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults.
Moreover, health literacy significantly influences an individual’s capacity to manage complex medication regimens. Patients with low health literacy may struggle to understand their treatment plans, increasing the likelihood of medication errors and adverse outcomes. This challenge underscores the necessity for healthcare providers to tailor communication strategies to patient understanding levels, thereby mitigating the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Simplified medication instructions and the use of aids such as pill organizers can be beneficial in enhancing medication adherence among these populations.
Lastly, societal trends towards self-medication and the ready availability of over-the-counter drugs contribute to polypharmacy. While self-medication can provide immediate relief for minor ailments, it can also result in unintended drug interactions and side effects. Proper guidance from healthcare professionals is crucial in preventing these potentially hazardous situations and curtailing the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults.
Effective Communication in Polypharmacy Management
Pertinent communication strategies are vital in addressing the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Effective patient-provider dialogue ensures that patients are well-informed about their prescribed treatments, fostering adherence and awareness. Educating patients on the significance of maintaining updated comprehensive medication lists and encouraging them to discuss all medications, including supplements and over-the-counter drugs, fortifies safety measures against adverse interactions.
Utilizing technology-driven solutions, such as electronic health records and patient portals, facilitates transparent communication between healthcare providers about patient medication regimens. This advancement supports prompt updates on prescription changes, curtailing the inadvertent continuation of medications that may exacerbate the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Furthermore, family members should be integrated into treatment discussions, providing additional support and acting as advocates for patient health and medication management.
Regular follow-up appointments enable healthcare providers to closely monitor patient responses to prescribed medication regimes. These consultations should involve a thorough assessment of potential side effects and any barriers to adherence, whether they be economic, cognitive, or emotional. By continuously addressing these concerns and maintaining open lines of communication, healthcare professionals can effectively mitigate the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults, ensuring optimal patient health outcomes.
Summary and Recommendations
In summary, the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults present a multifaceted challenge that necessitates comprehensive strategies for effective management. The increased risk of drug interactions and adverse effects requires diligent monitoring by healthcare providers. Regular medication reviews play an essential role in optimizing patient care and ensuring that medication regimens remain justified, necessary, and beneficial.
To further address the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults, it is imperative to enhance patient education efforts. By equipping patients with the knowledge to understand their medications and potential side effects, healthcare professionals foster higher adherence rates and empower patients to participate actively in their treatment plans. Further integration of technology into healthcare settings can streamline communication between providers and patients, ensuring cohesive care.
Ultimately, enhancing interprofessional collaboration among healthcare teams is crucial for minimizing the long-term effects of polypharmacy in adults. Open dialogue and shared decision-making result in a synchronized approach to patient care, facilitating timely interventions and eliminating medication redundancies. Only through these concerted efforts can the healthcare community effectively address and mitigate the implications of polypharmacy, improving patient outcomes and promoting safe pharmacotherapy across adult populations.