Pharmaceutical medications play a vital role in contemporary healthcare, addressing acute and chronic conditions and improving patients’ quality of life. However, the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications warrants careful consideration, given its potential implications for both individual health and broader societal impacts. It is essential for healthcare professionals to weigh the therapeutic benefits against potential risks when recommending prolonged use of these medications. This article delves into various aspects of long-term medication use, offering a comprehensive analysis of its implications and considerations.
Read Now : Challenges In Tissue Engineering Innovations
Implications of Prolonged Pharmaceutical Usage
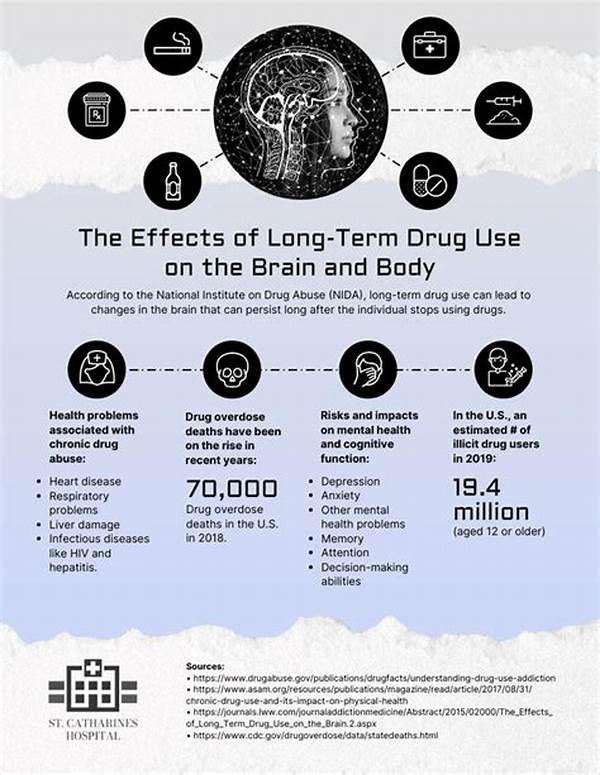
The long-term use of pharmaceutical medications can have significant effects on the health of patients. While these medications often provide necessary relief and management of chronic illnesses, they can also lead to various complications. Over time, the body may develop a tolerance, necessitating higher doses to achieve the same efficacy. Moreover, prolonged use increases the risk of side effects and potential dependency. Patients relying on these medications must be monitored closely to assess their overall health and to avert negative outcomes. The ultimate goal is to ensure that the benefits of medication significantly outweigh any adverse effects, providing a balanced approach to chronic disease management.
Healthcare providers face the challenge of tailoring medication regimens to individual patient needs while considering the broader implications of long-term use. It is crucial to regularly review the necessity and dosage of medications, exploring alternative treatments as appropriate. This vigilance helps in minimizing risks associated with prolonged medication use, such as organ damage or the development of secondary conditions. The decision-making process involves a collaborative effort between the patient and healthcare professionals, emphasizing informed choices and proactive management.
Considerations in Long-term Medication Use
1. Efficacy Maintenance: Ensuring that the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications continues to provide therapeutic benefits without diminishing effects is paramount for patient health.
2. Risk of Side Effects: Awareness and management of potential side effects are crucial, as these may compound with extended use, complicating patient outcomes.
3. Dependency Concerns: Long-term use can lead to physical or psychological reliance on medications, necessitating continuous evaluation and appropriate intervention strategies.
4. Patient Monitoring: Regular assessments by healthcare providers ensure ongoing evaluation of the necessity, effectiveness, and safety of the medication regimen.
5. Alternative Treatments: Exploration of non-pharmaceutical interventions may supplement or even replace long-term medication use, reducing risks and improving overall health outcomes.
Evaluating Long-term Use Outcomes
Healthcare practitioners must exercise diligence when prescribing medications for chronic conditions, taking into account the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications. Continuous evaluation of therapeutic benefits versus potential risks, such as adverse side effects or dependency issues, is critical. Additionally, a patient’s lifestyle, age, and medical history must be factored into this complex decision-making process. It is crucial for medical professionals to stay informed about the latest research and evolving guidelines to make well-rounded treatment decisions.
Implementing a patient-centric approach encourages active participation in the management of their healthcare, allowing for better communication and understanding of the long-term impacts of their medication regimen. Together with comprehensive monitoring, this engagement fosters a successful partnership between patients and healthcare providers, increasing the chances of achieving optimal outcomes in chronic disease management. Through this coordinated effort, the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications can be optimized to ensure maximum benefits with minimal adverse effects.
Understanding Medication Use through a Modern Lens
Alright, so when it comes to the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications, it’s all about finding that sweet spot between helping people out and keeping tabs on any potential downsides. You don’t want to mess with this stuff without knowing the ropes, right? Here’s the deal:
1. Staying sharp about how long-term meds can keep working for you.
2. Watching for any nasty side effects that might pop up.
3. Being chill about not getting too hooked on them pills.
4. Doctors gotta keep their eyes peeled, checking in on how folks are doing.
Read Now : Biomarkers Identification Through Genomics
5. Sometimes, maybe mix it up with some non-medical treatments.
6. It’s not just about the meds—consider lifestyle choices, you know?
7. Chatting with docs makes sure everyone’s on the same page.
8. Balancing benefits and risks? Yeah, that’s key.
9. New studies help you stay in the know about what works best.
10. In the end, it’s about keeping people healthy without overdoing it.
Reflecting on Pharmaceutical Strategies
In the realm of chronic disease treatment, the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications represents a critical element that demands responsible management. Medical professionals are tasked with revisiting medication plans regularly to ensure ongoing relevance and efficacy. This approach helps avoid potential over-reliance and mitigates any adverse side effects that may arise over time. A thoughtful evaluation process is vital for maintaining patient health and maximizing the effectiveness of prescribed treatments.
Long-term medication strategies should also incorporate lifestyle changes and preventive measures, thus enabling a holistic approach to health management. Encouraging patients to engage in healthier lifestyle choices can reduce dependence on medications over time. In doing so, healthcare providers not only enhance patient outcomes but also promote a sustainable healthcare model that prioritizes long-term well-being and self-care. A comprehensive understanding of the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications positions healthcare practitioners to advocate for balanced, effective treatment plans.
Navigating the Complexities of Long-term Medication Use
The world of long-term use of pharmaceutical medications is complex, requiring careful consideration from both healthcare professionals and patients. With the primary goal of optimizing patient health, it is imperative that medical practitioners continuously assess the pros and cons of sustained medication use. This involves evaluating not just the immediate effects but also potential long-term consequences that might affect a patient’s overall health status.
Two key considerations involve dosage adjustments and regular evaluations. Balancing the desired therapeutic outcomes with minimal side effects becomes paramount. Healthcare providers should work collaboratively with patients to adapt their treatment plans as necessary, especially in response to changes in health conditions or lifestyle factors. Through ongoing communication and assessment, both parties can navigate the intricacies of long-term medication use effectively, ensuring patient safety and improving quality of life over time.
Summary of Insights on Prolonged Medication Usage
In summary, the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications is a multifaceted aspect of modern healthcare that necessitates comprehensive evaluation and tailored management. By acknowledging the complexity involved, healthcare practitioners can devise appropriate strategies that mitigate risks such as side effects, dependency, and diminishing efficacy. Engaging in a continuous dialogue with patients fosters trust and collaboration, which are essential components in adapting treatment plans to suit evolving health needs.
Ultimately, the goal is to implement a balanced approach to medication management, integrating preventive measures and lifestyle modifications to enhance overall health. Healthcare practitioners should stay abreast of ongoing research and emerging guidelines to inform their practice. By doing so, the long-term use of pharmaceutical medications can be navigated successfully, ensuring positive outcomes for patients while promoting a sustainable, patient-focused healthcare system.