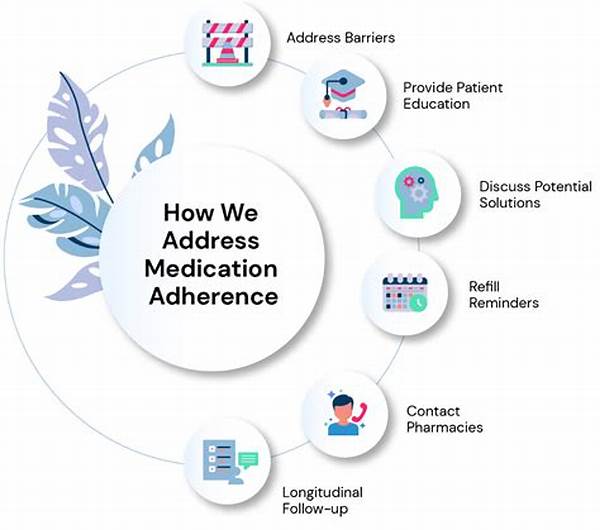
Medical adherence, defined as the extent to which a patient follows medical instructions, is a critical component in the healthcare continuum. The medical adherence importance cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts patient outcomes, influences healthcare costs, and determines the success of treatment plans. The necessity for adherence stems from the complex nature of diseases, especially chronic conditions, which demand consistent and precise medication intake over extended periods. Non-adherence can lead to disease progression, hospitalizations, and in severe cases, mortality. This underscores the need for increased awareness and education on medical adherence. Healthcare professionals must play a proactive role in encouraging patients to understand and commit to their prescribed regimens.
Read Now : **traditional Plant-based Healing**
Understanding Medical Adherence
Understanding the medical adherence importance is vital for both healthcare providers and patients. Medical adherence not only encompasses medication intake but also involves routine follow-ups, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments. Failure to adhere can diminish treatment efficacy and inflate healthcare costs. From a clinical standpoint, practitioners need to simplify regimens and communicate effectively to ensure patients comprehend the necessity of adherence. Also, empathy and patient engagement are fundamental in fostering trust and improving adherence rates. Health practitioners and stakeholders must employ strategies that promote sustained adherence, which, in turn, enhances the overall quality of patient care and health system efficiency.
Factors Influencing Adherence
1. Complexity of Medication Regimens: Simplified regimens can highlight the medical adherence importance by making it easier for patients to follow prescribed treatment plans.
2. Patient-Provider Communication: Effective communication within the healthcare setting emphasizes medical adherence importance, promoting better patient understanding and trust.
3. Socioeconomic Factors: Addressing barriers such as cost can augment the medical adherence importance by making medications accessible to all patient demographics.
4. Patient Education: An informed patient base underscores the medical adherence importance, leading to improved health outcomes.
5. Healthcare System Support: A supportive infrastructure that provides reminders and follow-up care can amplify the medical adherence importance and enhance adherence rates.
Read Now : Strategies For Clear Medical Dialogues
Strategies to Improve Medical Adherence
Improving patient adherence involves a multi-faceted approach that incorporates education, communication, and system-wide support. Recognizing the medical adherence importance requires healthcare systems to develop personalized interventions tailored to individual patient needs. This includes clear patient education to ensure a thorough understanding of their medical regimens and potential side effects. Additionally, healthcare professionals should employ technology such as mobile apps and digital reminders designed to aid patients in tracking their medication schedules. Establishing a supportive healthcare environment further reinforces medical adherence, as patients are more likely to adhere to regimens in a system they trust. Multi-disciplinary collaboration among healthcare providers fosters a unified approach toward adherence, ultimately leading to enhanced patient outcomes and the optimization of healthcare resources.
Perspectives on Medical Adherence Importance
Clinician’s Approach
From a clinician’s perspective, reinforcing the medical adherence importance begins with understanding and addressing individual patient barriers. This might involve offering simplified treatment plans or facilitating access to medication. Healthcare providers must spearhead efforts to identify patients at risk of non-adherence and institute preventive measures. Moreover, the integration of routine check-ups and personalized care plans can ensure continuity in adherence strategies. Clinicians are encouraged to harness technological solutions, such as electronic adherence monitoring, to track patient progress. In collaboration with patients, clinicians can cultivate an adherence-focused culture, which not only reduces the burden of disease but also elevates the standards of patient care and treatment outcomes.
The Patient’s Role
Patients play a pivotal role in understanding the medical adherence importance. Empowered by accurate information and resources, patients can actively participate in their treatment journeys. It is imperative for patients to be honest with healthcare providers about their challenges and experiences with medication adherence. Developing a patient-centric adherence approach underscores the need for patients to establish open communication lines with their healthcare team. This collaboration aids in addressing any concerns and modifying treatment plans accordingly. Patients should also aim to be proactive in maintaining an organized regimen through the use of tools, such as medication calendars or smartphone reminders, which help keep them compliant with their prescribed therapies, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Summary of Medical Adherence Importance
In summary, the medical adherence importance cannot be overemphasized, given its direct effects on therapy success rates, patient health, and overall healthcare system efficiency. By examining various contributing factors and strategies to bolster adherence, both patients and healthcare providers can work together to bridge adherence gaps. The enhancement of medical adherence involves a collaborative effort driven by effective communication, education, and the implementation of innovative technologies. Through this approach, the healthcare system can achieve not only better patient outcomes but also a reduction in healthcare costs and an elevation in the quality of care provided. Understanding and fostering medical adherence is a shared responsibility that underpins the future of medical treatment effectiveness and patient satisfaction.