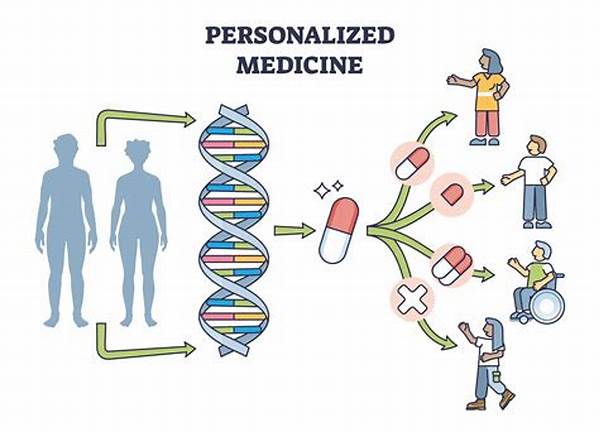
In recent years, the advent of personalized medicine using genomics has profoundly transformed the landscape of healthcare. This innovative approach tailors medical treatment to the individual characteristics of each patient, enhancing the precision and effectiveness of interventions. By leveraging genomic information, healthcare providers are now better equipped to predict disease susceptibility, tailor therapies, and improve patient outcomes, representing a significant shift from the traditional one-size-fits-all model of medicine. The integration of genomic data into clinical practice marks a promising path forward, with potential applications across various medical disciplines.
Read Now : Immediate Pain Alleviation Strategies
The Role of Genomics in Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine using genomics is at the forefront of a healthcare revolution. By deciphering the genetic blueprint of individuals, it enables the customization of medical treatments to match specific genetic profiles. Through detailed genetic analysis, practitioners can identify genetic mutations and variations that may predispose individuals to certain diseases or affect responses to medications. This personalized approach not only facilitates the design of targeted therapies but also plays a crucial role in preventive healthcare by identifying individuals at high risk for specific conditions. As the field continues to evolve, the implementation of personalized medicine using genomics holds the promise of transforming patient care, improving health outcomes, and optimizing therapeutic strategies.
Moreover, personalized medicine using genomics impacts disease diagnosis by offering insights into genetic predispositions and anomalies. It allows for the early detection of diseases, often before symptoms manifest, enabling more timely and effective interventions. In oncology, for example, genomic profiling of tumors can inform the selection of precise treatment regimens, enhancing efficacy while minimizing adverse effects. As research in genomics progresses, its application in personalized medicine is expected to expand, potentially leading to breakthroughs in understanding complex diseases and refining preventive strategies.
Benefits of Personalized Medicine Using Genomics
1. Personalized medicine using genomics offers improved treatment efficacy by aligning therapies with individual genetic profiles, reducing the variability in treatment responses.
2. By identifying genetic predispositions, personalized medicine using genomics facilitates early intervention and preventive strategies, potentially reducing disease incidence and improving long-term health outcomes.
3. Personalized medicine using genomics aids in minimizing adverse drug reactions, as genetic insights can predict individual responses to specific medications.
4. It enhances patient empowerment by providing insights into personal health risks, encouraging proactive engagement in healthcare decisions.
5. Personalized medicine using genomics fosters innovation in therapeutic development, driving the creation of novel, targeted treatments designed for specific genetic markers.
Challenges and Opportunities in Implementing Genomics
The implementation of personalized medicine using genomics presents both challenges and opportunities. One of the primary challenges is the need for robust infrastructure to support the integration of genomic data into clinical practice. This includes the establishment of comprehensive databases, advanced diagnostic tools, and specialized training for healthcare professionals. Additionally, ethical considerations surrounding patient privacy and data security necessitate stringent regulatory frameworks to safeguard sensitive genetic information.
Despite these challenges, the opportunities presented by personalized medicine using genomics are substantial. The capacity to tailor treatments to genetic profiles not only promises more effective therapies but also fosters a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms. Furthermore, as genomic technologies become more accessible, there is potential for increased healthcare equity, enabling broader populations to benefit from personalized approaches. Advances in genomic research and technology are expected to drive the evolution of healthcare, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and a more sustainable healthcare system.
Understanding Personalized Medicine Using Genomics: A Layman’s Guide
Alright, so, personalized medicine using genomics is all about getting the right treatment for YOU by looking at your genes. Think of it as a super-customized medical approach. Instead of a blanket solution, doctors check out your DNA to figure out what might work best for you. This means fewer side effects because the treatment is really tuned for how you tick genetically. It’s like having a playlist of songs that perfectly matches your vibe instead of just listening to whatever’s trending. Personalized medicine using genomics is making healthcare way more personal and specific!
1. This cutting-edge tech translates to smart treatments planned just for you. Thanks to personalized medicine using genomics, all based on your genetic make-up.
2. Big win here is foreseeing health issues before they happen by peeping into those genes.
3. Less “Uh-oh, this medicine doesn’t work for me” moments – because they’re using personalized medicine using genomics.
4. Personalized medicine using genomics lets you in on what your body needs by deciphering your genetic story.
Read Now : **robotic-assisted Surgical Systems**
5. Navigating health becomes like having your personalized GPS, guiding you precisely where you need to go.
6. It’s not just about being sick – prevention is a big perk of personalized medicine using genomics.
7. The future health game? Getting your genes to talk and adjusting your medical playlist accordingly.
8. Knowing what could go down health-wise puts you in the driver’s seat of wellness decisions.
9. Tech keeps getting cooler, making personalized medicine using genomics a feasible reality for way more folks.
10. Bottom line: It’s about making health care less “general” and more “generally awesome” by being tailor-made.
Advancements in Genomic Technologies for Personalized Medicine
In the current landscape of medical advancement, personalized medicine using genomics stands as a beacon of progress, leveraged by significant technological innovations. Genomic sequencing technologies, for instance, have dramatically decreased in cost and increased in speed, enabling the comprehensive analysis of genetic material. This profound advancement allows for the extensive mapping of an individual’s genetic blueprint, facilitating the identification of genetic markers that influence disease susceptibility and treatment response. As a result, personalized medicine using genomics can provide tailored therapeutic strategies that enhance treatment efficacy and minimize adverse effects.
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into genomic analysis further bolsters the capabilities of personalized medicine using genomics. These technologies enable the rapid processing and interpretation of complex genomic data, identifying patterns and correlations that may not be immediately apparent to human analysis. Consequently, healthcare practitioners can develop targeted interventions with a higher degree of precision. Moreover, ongoing research and collaborations between academia, healthcare, and biotech industries continue to drive the refinement and implementation of these tools, broadening the scope of personalized medicine using genomics and paving the way for more nuanced, individualized approaches in disease management.
Ethical Considerations in Personalized Medicine Using Genomics
Personalized medicine using genomics, while offering significant advancements in medical care, necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The collection and utilization of genetic data raise concerns regarding patient privacy and data protection. Ensuring that genomic information is securely stored and accessed only by authorized personnel is paramount to maintaining patient trust and confidentiality. Additionally, informed consent processes must be rigorous, providing patients with a clear understanding of how their genetic information will be used and the potential implications for their health and that of their relatives.
Equity and access pose further ethical challenges in the realm of personalized medicine using genomics. The benefits of genomic-based treatments must be accessible to diverse populations, irrespective of socioeconomic status or geographical location. This requires concerted efforts to bridge disparities in healthcare access and to ensure that advances in genomics enhance health outcomes for all populations equitably. Addressing these ethical concerns is crucial not only to safeguard patient interests but also to promote the responsible and inclusive adoption of personalized medicine using genomics, thereby maximizing its benefits for society at large.
Concluding Insights on Personalized Medicine Using Genomics
In conclusion, personalized medicine using genomics represents a pivotal shift towards more effective and individualized healthcare. By harnessing genomic information, medical practitioners can deliver interventions that are not only precisely tailored to the genetic profiles of patients but also predictive and preventive in nature. This transformative approach has the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes by optimizing therapeutic efficacy and minimizing adverse reactions.
As genomic technologies advance and become more integrated into mainstream healthcare, the impact of personalized medicine using genomics is expected to grow. However, the realization of this promise necessitates addressing ethical, infrastructural, and educational challenges. Collaborative efforts from all stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem are essential to ensure that the implementation of personalized medicine using genomics is both equitable and effective, setting the stage for a future where healthcare is truly personalized to the individual needs of every patient.