Vaccinations have played a pivotal role in modern medicine, serving as a cornerstone in the prevention of infectious diseases. With the advent of vaccines, humanity has witnessed a significant reduction in the incidence of debilitating illnesses, safeguarding generations from the ravages of pathogens. In the context of public health, the role of vaccinations in prevention cannot be overstated as they offer an effective means to control the spread of diseases and protect vulnerable populations.
Read Now : What Is The Purpose Of Modern Medicine
The Historical Context of Vaccines
The role of vaccinations in prevention can be traced back to the late 18th century when Edward Jenner discovered the smallpox vaccine. This groundbreaking discovery set the stage for the development of numerous vaccines that have since eradicated smallpox and significantly diminished the prevalence of diseases like polio and measles. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and combat pathogens effectively. This immunological priming not only benefits the individual recipient but also contributes to herd immunity, reducing the likelihood of outbreaks within the community.
The importance of the role of vaccinations in prevention extends to their ability to adapt to emerging threats. The continuous study and evolution of vaccines ensure that they can address new strains of existing pathogens and novel infectious agents. This dynamic capability of vaccines highlights their significance in an ever-changing microbial landscape, underscoring the need for ongoing research and development.
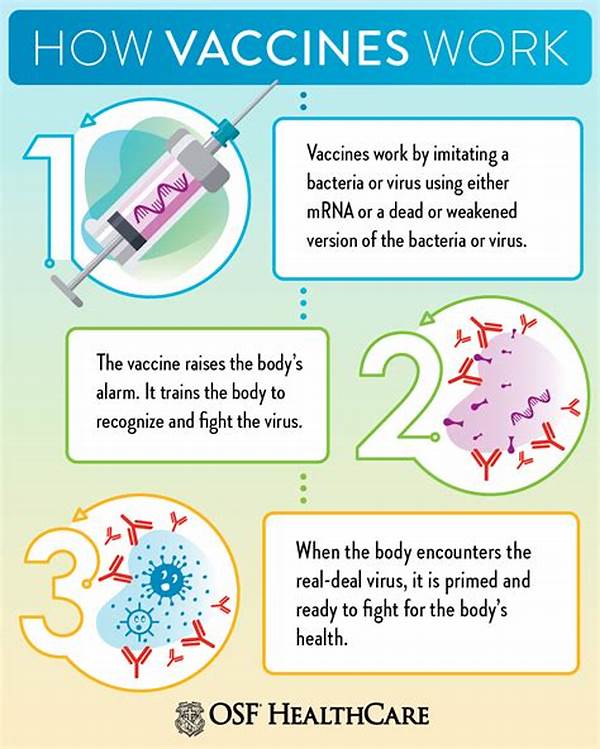
Mechanisms of Vaccine Action
1. Pathogen Recognition: The role of vaccinations in prevention is fundamentally based on the immune system’s ability to recognize foreign pathogens. Vaccines introduce harmless components or weakened forms of these pathogens, prompting an immune response without causing disease.
2. Immune Memory Formation: A critical role of vaccinations in prevention is the development of immune memory. This ensures a rapid and effective response upon actual exposure to the pathogen, significantly reducing the risk of infection.
3. Herd Immunity: By immunizing a significant portion of the population, the role of vaccinations in prevention extends to protecting those who are unvaccinated or unable to receive vaccines, thus preventing the spread of infectious diseases.
4. Reduction of Disease Burden: The role of vaccinations in prevention can be seen in the reduced incidence and severity of diseases. This leads to fewer healthcare resources being needed for treatment and contributes to overall public health improvement.
5. Mitigation of Economic Impact: Vaccinations contribute to economic stability by preventing outbreaks that can lead to loss of productivity and strained healthcare systems. The role of vaccinations in prevention thus spans beyond health, impacting socioeconomic factors.
Public Health and Vaccination Campaigns
The role of vaccinations in prevention is critical to public health strategies worldwide. National and international agencies focus on increasing vaccine accessibility and coverage to ensure broad protection against preventable diseases. Mass vaccination campaigns have played a crucial role in the near-eradication of diseases such as polio, which once posed significant global health challenges. These campaigns emphasize the importance of continued vaccination efforts, particularly in regions with limited healthcare infrastructure, to sustain gains made in disease control.
In addition to individual protection, the role of vaccinations in prevention includes the safeguarding of entire communities. Vaccination programs aim to achieve high levels of immunity to disrupt chain transmissions of infectious agents. This community-level approach is paramount in maintaining public health and secures a quality life for all by preventing the resurgence of previously controlled diseases.
Addressing Misconceptions and Increasing Vaccine Acceptance
Public perception of vaccinations critically influences their success. The role of vaccinations in prevention can be undermined by misinformation which sows doubt and leads to vaccine hesitancy. Educating the public on the safety and efficacy of vaccines is essential. Reliable information from high-quality research and transparent communication from health authorities is imperative to build trust and increase vaccination uptake.
Read Now : Health Impacts Of Combining Prescriptions
Acknowledging cultural sensitivity and regional beliefs also plays a role in facilitating effective vaccination campaigns. Tailored messaging that respects diverse perspectives contributes to higher acceptance levels. Overall, the role of vaccinations in prevention is dependent on a multi-faceted approach that involves scientific innovation, public education, and community engagement endeavors.
Strategies for Enhancing Vaccination Rates
The role of vaccinations in prevention is amplified through strategic initiatives aimed at improving vaccination rates. One approach involves creating awareness campaigns that educate the masses about vaccine benefits, risks of non-vaccination, and the scientific rigor underpinning vaccine development. By increasing knowledge and understanding, such initiatives work to dispel myths and build public confidence in immunization programs.
Moreover, collaboration between governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) enhances vaccination reach and accessibility, particularly in underserved areas. The integration of vaccines into primary healthcare services ensures that populations have regular, equitable access to immunization. Furthermore, incentivizing healthcare providers to meet vaccination targets has proven to be an effective strategy for reducing vaccine-preventable diseases.
The Economic Impact of Vaccination Initiatives
The role of vaccinations in prevention is far-reaching with significant economic implications. By preventing diseases, vaccinations reduce the need for medical treatments and hospitalizations, which in turn alleviates pressure on healthcare systems. This prevention translates to substantial cost savings for governments and society alike. Furthermore, a healthier population enhances economic productivity, with fewer workdays lost to illness and improved quality of life.
Implementing effective vaccination initiatives also plays a crucial role in global public health priorities, such as reducing mortality rates among children and promoting sustainable development. As vaccines continue to evolve and adapt to emerging health challenges, their preventive role becomes increasingly essential, reaffirming the need for sustained investment and innovation in immunization programs.
Summary and Implications
In conclusion, the role of vaccinations in prevention is, without doubt, a cornerstone of global health strategies. By harnessing the body’s natural defense mechanisms, vaccines provide crucial protection against numerous infectious diseases. Beyond individual well-being, vaccinations enhance public health through the establishment of herd immunity and contribute to global efforts to eradicate diseases.
The continued success of vaccinations in preventing disease hinges on several factors including scientific advancements, public acceptance, and collaborative international health policies. Addressing challenges such as vaccine hesitancy and ensuring equitable distribution remains pivotal. As health paradigms evolve, the role of vaccinations in prevention will continue to be central to safeguarding the health of future generations and promoting a resilient, healthier world.