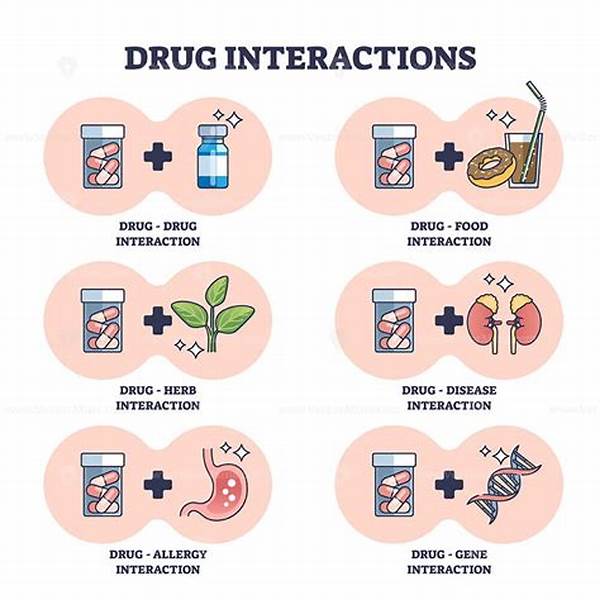
Mixing multiple medications can lead to significant health risks and should be approached with caution. Understanding the side effects of mixing multiple medicines is crucial for ensuring patient safety and optimizing therapeutic outcomes. Healthcare professionals and patients must be informed about the potential interactions and adverse reactions that can arise from polypharmacy.
Read Now : Safe Herb-drug Combinations List
Understanding the Risks
The side effects of mixing multiple medicines often stem from drug interactions, which can alter the effects of the medications involved. This phenomenon can lead to increased toxicity, reduced therapeutic efficacy, or the emergence of unexpected adverse reactions. It is imperative for individuals prescribed multiple medications to regularly consult with healthcare providers to review their medication regimen. Regular consultation can help identify any potentially harmful interactions and allow for timely adjustments. Being proactive in managing medication interactions not only enhances patient safety but also improves the likelihood of achieving desired treatment outcomes. Moreover, understanding the side effects of mixing multiple medicines can help patients and healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding treatment plans, balancing benefits against risks.
Common Interactions and Consequences
1. Antagonistic Effects: Some medications can cancel out each other’s effects, minimizing their efficacy.
2. Synergistic Toxicity: Combining drugs with similar effects can lead to overdose.
3. Altered Metabolism: One drug can accelerate or inhibit the metabolism of another, affecting drug levels in the body.
4. Increased Side Effects: Mixing multiple medicines can amplify common side effects, such as drowsiness or nausea.
5. Unanticipated Reactions: New, unexpected side effects may emerge when medications interact.
Monitoring and Management
Monitoring and managing the side effects of mixing multiple medicines require vigilance and cooperation among patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers. Health professionals should conduct thorough medication reviews, taking into account all prescribed, over-the-counter, and herbal supplements a patient may be taking. Utilizing electronic health records and decision-support systems can aid in identifying potential drug interactions. Patients should be encouraged to disclose all medications they are using, including non-prescription remedies, to their healthcare providers. Educating patients about recognizing early signs of adverse reactions is pivotal in preventing severe outcomes. In some cases, alternative therapies or dosage adjustments may be necessary to mitigate the side effects of mixing multiple medicines.
Read Now : Genomic Analysis For Personalized Care
Patient Awareness and Education
Promoting awareness regarding the side effects of mixing multiple medicines is essential for patient safety. Patients must be educated about the potential risks associated with polypharmacy and the importance of adhering to prescribed doses. Encouraging active communication between patients and healthcare providers can foster better understanding and management of medication regimens. Information campaigns and educational resources can serve as valuable tools in enhancing patient knowledge and minimizing the risk of adverse interactions. By understanding the side effects of mixing multiple medicines, patients can actively participate in their healthcare decisions, thereby improving overall treatment efficacy and safety.
Communication and Collaboration
Enhancing Patient-Provider Communication
Effective communication between patients and healthcare providers is paramount in managing the side effects of mixing multiple medicines. Patients should feel empowered to openly discuss their concerns and symptoms with their healthcare teams. In turn, healthcare providers should actively listen, provide clear explanations, and consider patient preferences and experiences when formulating treatment plans. Collaborative decision-making not only enhances patient satisfaction but also contributes to more effective management of medication-related risks.
Technological Support in Drug Management
Advancements in technology have greatly benefited the management of the side effects of mixing multiple medicines. Electronic prescribing systems, drug interaction checkers, and clinical decision support tools are invaluable resources for healthcare providers. These technologies enable the quick identification of potential interactions and facilitate safer prescribing practices. Patients can also benefit from mobile health applications that track medication schedules, remind users of doses, and provide information on potential side effects, further aiding in the safe use of multiple medications.
Summary and Outlook
In conclusion, the side effects of mixing multiple medicines remain a significant concern in the realm of healthcare. Understanding the potential interactions and associated risks is essential for ensuring patient safety and optimizing treatment outcomes. Through comprehensive education, effective communication, and the utilization of technological advancements, healthcare providers and patients can work collaboratively to mitigate the risks associated with polypharmacy. Encouraging open dialogue and proactive management strategies will continue to play a vital role in addressing the complexities of mixing multiple medications. As the landscape of medicine evolves, ongoing research and practice updates will be vital in refining approaches to minimize the adverse effects and maximize the therapeutic benefits of medication regimens.