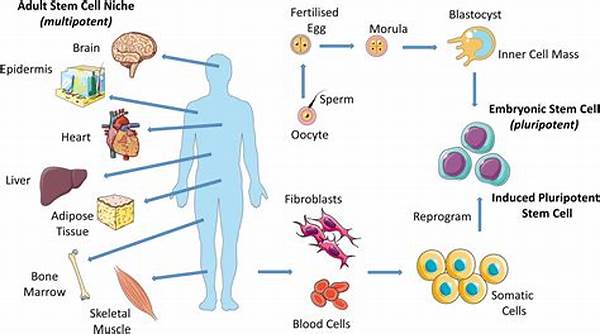
The advent of stem cell research marks a pivotal milestone in regenerative medicine, offering profound insights into the body’s self-repair mechanisms. Stem cells hold the extraordinary potential to transform into various cell types, paving the way for innovative treatments for a myriad of ailments. A deeper understanding of the stem cell role in organ regeneration unveils new horizons for medical science, potentially heralding a new era in treating organ failure and diseases.
Read Now : Data Security In Healthcare Solutions
Mechanisms of Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
Understanding the mechanisms underlying the stem cell role in organ regeneration is critical for advancing therapeutic applications. Stem cells, particularly pluripotent stem cells, can differentiate into any cell type, making them invaluable in regenerating damaged tissues and organs. This unique ability stems from their intrinsic capacities for self-renewal and pluripotency, which enable the replenishment of lost or damaged cells.
Central to the stem cell role in organ regeneration is the activation and navigation of signaling pathways that dictate cell fate. Crucial signals, such as growth factors and environmental cues, direct stem cells to specific differentiation paths, ensuring the functional integration of newly formed cells within the organ’s architecture. Additionally, the interaction between stem cells and their niche—the specialized microenvironment—plays a pivotal role in maintaining stem cell functions and orchestrating tissue regeneration. Thus, harnessing these mechanisms may unlock unprecedented potential in treating degenerative diseases and organ failure.
Challenges in Utilizing Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
1. Ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks often challenge the implementation of research involving the stem cell role in organ regeneration, necessitating stringent oversight.
2. Technical complexities in manipulating stem cells require advanced methodologies to ensure the efficacy and safety of regenerative therapies.
3. Immunological barriers, such as immune rejection, present significant hurdles for the stem cell role in organ regeneration.
4. Scalability and the economic viability of stem cell-based interventions remain formidable challenges.
5. Long-term stability and integration of regenerated tissues necessitate comprehensive evaluations to affirm the safety of the stem cell role in organ regeneration.
Innovations in Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
Recent advancements in biotechnology have revolutionized the application of the stem cell role in organ regeneration. State-of-the-art gene editing techniques, such as CRISPR-Cas9, enable precise modifications of stem cells, enhancing their regenerative capabilities and mitigating risks associated with uncontrolled differentiation. Moreover, the development of organoids—miniaturized, simplified versions of organs grown in vitro—provides valuable models for studying developmental processes and diseases. These innovations underpin the potential transformation of regenerative medicine, offering hope for patients requiring organ transplants or suffering from chronic conditions.
The combination of tissue engineering and stem cell research is forging a new frontier in personalized medicine, developing patient-specific therapies to address unique clinical needs. Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations are accelerating the translation of these innovations from bench to bedside, heralding a new dawn in medical treatment paradigms. As research progresses, the potential to personalize interventions based on individual genetic and molecular profiles highlights the transformative nature of the stem cell role in organ regeneration.
Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration: Unveiling Prospects
Okay, so picture this: your body’s got this insane ability to fix itself, thanks to the stem cell role in organ regeneration! These nifty cells can turn into almost any type of cell your body needs. It’s like having a backstage pass to your body’s own repair shop. Here’s the lowdown:
1. Stem cells are like blank canvases – they can become any cell.
2. Scientists are totally stoked about these cells transforming medicine.
3. Some folks worry about the ethics, but the benefits could be massive.
4. Stem cells could, legit, replace busted organs.
Read Now : Individualized Herb-based Healthcare
5. This could mean no more waitlists for organ donors. Sweet, right?
6. Researchers are figuring out how to use these without complications.
7. Costs? Yeah, they need to figure that out, too.
8. Even diseases that have stumped scientists could find a cure.
9. The tech is moving fast – like blink, and you’ll miss it fast.
10. Bottom line: the stem cell role in organ regeneration is the future!
Potential Impact of Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
The potential impact of the stem cell role in organ regeneration is monumental, offering solutions to previously insurmountable medical challenges. With their unique capability to continuously divide and transform into specialized cells, stem cells are at the forefront of efforts to regenerate organs damaged by injury or disease. By developing methodologies to precisely control the differentiation of stem cells, researchers can potentially overcome limitations posed by current treatment modalities.
The integration of multi-disciplinary scientific approaches enriches our understanding of stem cell dynamics and regenerative processes. Advances in molecular biology and bioinformatics have facilitated the identification of critical pathways that govern stem cell behavior. Consequently, such insights empower scientists to refine strategies for improving the efficacy and predictability of stem cell-based therapies. As these innovations gain traction, they promise a future wherein the stem cell role in organ regeneration becomes an integral component of standard medical practices.
Ethical Implications of Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
The ethical landscape surrounding the stem cell role in organ regeneration remains complex, demanding ongoing discourse and examination. Central to these discussions are the moral considerations inherent in deriving stem cells from various sources, particularly embryonic stem cells. Balancing scientific exploration with ethical responsibility is crucial for ensuring that progress in this field aligns with societal values.
Guidelines and regulations governing stem cell research aim to protect all stakeholders while fostering an environment conducive to innovation. By promoting transparent decision-making and inclusive dialogue, the scientific community can navigate the ethical intricacies associated with stem cell technologies. As advancements continue to unfold, an unwavering commitment to ethical integrity will be paramount in realizing the full potential of the stem cell role in organ regeneration.
Conclusion on Stem Cell Role in Organ Regeneration
In summary, the stem cell role in organ regeneration represents a paradigm shift in medical science, with profound implications for patient care and therapeutic strategies. Its capacity to innovate and transform treatment approaches creates an expectation of enhanced health outcomes and longevity for individuals afflicted by severe organ damage. The continued expansion of research in this domain is essential to harness its capabilities fully.
As we look to the future, a collaborative approach involving researchers, clinicians, ethicists, and policymakers will be indispensable in unlocking the full promise of stem cell technologies. Through continued innovation and ethical stewardship, the stem cell role in organ regeneration is poised to redefine boundaries in medicine, offering hope and healing to patients worldwide.